Naive Bayes Exercise-程序员宅基地
技术标签: Naive Bayes Machine Learning
本文将通过朴素贝叶斯解决邮件的分类问题。理论文献参考:http://openclassroom.stanford.edu/MainFolder/DocumentPage.php?course=MachineLearning&doc=exercises/ex6/ex6.html。文章将分为三个部分,首先介绍一下基本的概率概念,然后对给出了特征的邮件进行分类,最后给出邮件特征的提取代码。
概率知识
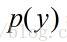 表示在一系列事件(数据)中发生y 的概率。
表示在一系列事件(数据)中发生y 的概率。
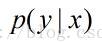 表示给定x 后,发生y 的概率。
表示给定x 后,发生y 的概率。

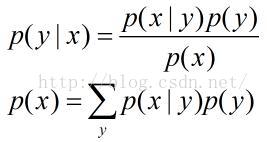
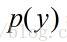 称之为先验概率,即不需要考虑x 的影响;
称之为先验概率,即不需要考虑x 的影响;
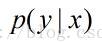 表示给定x 后,发生y 的概率,故称之为y 的后验概率。
表示给定x 后,发生y 的概率,故称之为y 的后验概率。
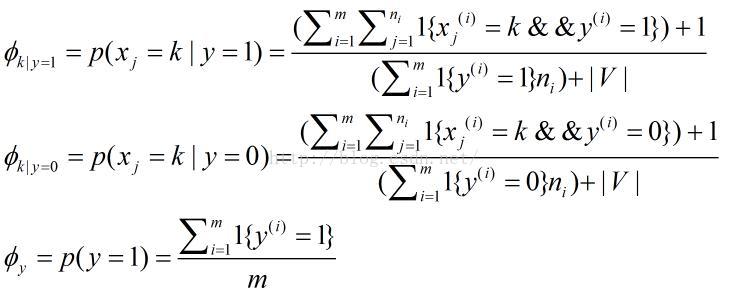
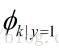 表示在一封垃圾邮件中给定单词是字典中第k个单词的概率;
表示在一封垃圾邮件中给定单词是字典中第k个单词的概率;
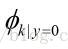 表示在一封非垃圾邮件中给定单词是字典中第k个单词的概率;
表示在一封非垃圾邮件中给定单词是字典中第k个单词的概率;
 表示训练邮件中垃圾邮件所占概率;
表示训练邮件中垃圾邮件所占概率;
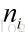 个单词,字典中包含
个单词,字典中包含
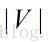 个单词。
个单词。
邮件分类
clc, clear;
% Load the features
numTrainDocs = 700;
numTokens = 2500;
M = dlmread('train-features.txt', ' ');
spmatrix = sparse(M(:,1), M(:,2), M(:,3), numTrainDocs, numTokens); % size: numTrainDocs * numTokens
% row: document numbers
% col: words in dirctionary
% element: occurrences
train_matrix = full(spmatrix);
% Load the labels for training set
train_labels = dlmread('train-labels.txt'); % i-th label corresponds to the i-th row in train_matrix
% Train
% 1. Calculate \phi_y
phi_y = sum(train_labels) ./ length(train_labels);
% 2. Calculate each \phi_k|y=1 for each dictionary word and store the all
% result in a vector
spam_index = find(1 == train_labels);
nonspam_index = find(0 == train_labels);
spam_sum = sum(train_matrix(spam_index, :));
nonspam_sum = sum(train_matrix(nonspam_index, :));
phi_k_y1 = (spam_sum + 1) ./ (sum(spam_sum) + numTokens);
phi_k_y0 = (nonspam_sum + 1) ./ (sum(nonspam_sum) + numTokens);
% Test set
test_features = dlmread('test-features.txt');
spmatrix = sparse(test_features(:,1), test_features(:,2),test_features(:,3));
test_matrix = full(spmatrix);
numTestDocs = size(test_matrix, 1);
% Calculate probability
prob_spam = log(test_matrix * phi_k_y1') + log(phi_y);
prob_nonspam = log(test_matrix * phi_k_y0') + log(1 - phi_y);
output = prob_spam > prob_nonspam;
% Read the correct labels of the test set
test_labels = dlmread('test-labels.txt');
% Compute the error on the test set
% A document is misclassified if it's predicted label is different from
% the actual label, so count the number of 1's from an exclusive "or"
numdocs_wrong = sum(xor(output, test_labels))
%Print out error statistics on the test set
error = numdocs_wrong/numTestDocs<pre name="code" class="plain">log_a = test_matrix*(log(prob_tokens_spam))' + log(prob_spam);
log_b = test_matrix*(log(prob_tokens_nonspam))'+ log(1 - prob_spam); 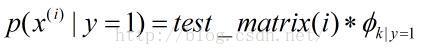 ,即对于每一个特征单词求总的概率
,即对于每一个特征单词求总的概率
log_a = log(test_matrix * prob_tokens_spam') + log(prob_spam);
log_b = log(test_matrix * prob_tokens_nonspam')+ log(1 - prob_spam); 特征单词提取
clc;clear
% This file extracts features of emails for judging whether an email is a
% spam or not.
%% Read all text files in cell variable 'data'
data = cell(0);
directory = dir('.');
numberDirect = length(directory);
for n = 3 : numberDirect
files = dir(directory(n).name);
numberFiles = length(files);
for i = 3 : numberFiles
% Be careful the path
fid = fopen(['.\', directory(n).name, '\', files(i).name]);
if (-1 == fid)
fclose(fid);
continue;
end
dataTemp = textscan(fid, '%s', '\n');
fclose(fid);
data = [data; dataTemp{1, 1}];
end
end
%% Sort the data by alphabet.
data = sort(data);
% Count occurrences and delete duplicate words and store in a struct variable.
numberStrings = length(data);
words = struct('strings', {}, 'occurrences', 0);
numberFeature = 1;
occurrences = 1;
for i = 1 : numberStrings - 1
if (strcmp(char(data(i)), char(data(i + 1))))
occurrences = occurrences + 1;
else
words(numberFeature).strings = char(data(i));
words(numberFeature).occurrences = occurrences;
numberFeature = numberFeature + 1;
occurrences = 1;
end
end
words = struct2cell(words);
%% This is only for testing, or you can use
% 'sortrows(cell2mat(words(2, 1, :)))' for getting the 2500 most words.
orders = ones(numberFeature - 1, 1);
for i = 2 : numberFeature - 1
orders(i) = orders(i) + orders(i - 1);
end
features_number = cell2mat(words(2, 1, :));
features_numbers = [features_number(:), orders];
%% Get the 2500 most words to generate dictionary
features_numbers = sortrows(features_numbers);
directionary = words(:, :, features_numbers(:, 2));
directionary = directionary(1, 1, end - 2500 : end - 1);
directionary = sort(directionary(:));
%% calculate features in all folders for trainset and testset
for n = 3 : numberDirect
files = dir(directory(n).name);
numberFiles = length(files);
for i = 3 : numberFiles
fid = fopen(['.\', directory(n).name, '\', files(i).name]);
if (-1 == fid)
fclose(fid);
continue;
end
dataTemp = textscan(fid, '%s', '\n');
fclose(fid);
data = dataTemp{1,1};
feature = find_indexandcount(data, directionary);
docnumber = (i - 2) * ones(size(feature, 1), 1);
featrues = [docnumber, feature];
if (3 == i)
dlmwrite(['.\', directory(n).name, '\', 'features.txt'], featrues, 'delimiter', ' ');
else
dlmwrite(['.\', directory(n).name, '\', 'features.txt'], featrues, '-append', 'delimiter', ' ');
end
end
endfunction result = find_indexandcount(email, dictionary)
% This function computes words' index and count in an email by a dictionary.
numberStrings = length(email);
numberWords = length(dictionary);
count = zeros(length(dictionary), 1);
for i = 1 : numberStrings
count = count + strcmp(email(i), dictionary);
end
% Record order sequence
orders = ones(numberWords, 1);
for i = 2 : length(dictionary) - 1
orders(i) = orders(i) + orders(i - 1);
end
result = sortrows([orders, count], 2);
% Find words which appear more than 1 times
reserve = find(result(:, 2));
result = result(reserve, :);
end% train.m
% Exercise 6: Naive Bayes text classifier
clear all; close all; clc
% store the number of training examples
numTrainDocs = 350;
% store the dictionary size
numTokens = 2500;
% read the features matrix
M0 = dlmread('nonspam_features_train.txt', ' ');
M1 = dlmread('spam_features_train.txt', ' ');
nonspmatrix = sparse(M0(:,1), M0(:,2), M0(:,3), numTrainDocs, numTokens);
nonspamtrain_matrix = full(nonspmatrix);
spmatrix = sparse(M1(:,1), M1(:,2), M1(:,3), numTrainDocs, numTokens);
spamtrain_matrix = full(spmatrix);
% Calculate probability of spam
phi_y = size(spamtrain_matrix, 1) / (size(spamtrain_matrix, 1) + size(nonspamtrain_matrix, 1));
spam_sum = sum(spamtrain_matrix);
nonspam_sum = sum(nonspamtrain_matrix);
% the k-th entry of prob_tokens_spam represents phi_(k|y=1)
phi_k_y1 = (spam_sum + 1) ./ (sum(spam_sum) + numTokens);
% the k-th entry of prob_tokens_nonspam represents phi_(k|y=0)
phi_k_y0 = (nonspam_sum + 1) ./ (sum(nonspam_sum) + numTokens);
% Test set
test_features_spam = dlmread('spam_features_test.txt',' ');
test_features_nonspam = dlmread('nonspam_features_test.txt',' ');
numTestDocs = max(test_features_spam(:,1));
spmatrix = sparse(test_features_spam(:,1), test_features_spam(:,2),test_features_spam(:,3),numTestDocs, numTokens);
nonspmatrix = sparse(test_features_nonspam(:,1), test_features_nonspam(:,2),test_features_nonspam(:,3),numTestDocs,numTokens);
test_matrix = [full(spmatrix); full(nonspmatrix)];
% Calculate probability
prob_spam = log(test_matrix * phi_k_y1') + log(phi_y);
prob_nonspam = log(test_matrix * phi_k_y0') + log(1 - phi_y);
output = prob_spam > prob_nonspam;
% Compute the error on the test set
test_labels = [ones(numTestDocs, 1); zeros(numTestDocs, 1)];
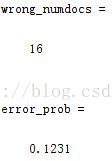
wrong_numdocs = sum(xor(output, test_labels))
%Print out error statistics on the test set
error_prob = wrong_numdocs/numTestDocs
其结果如下:(分类错误的个数及概率)
智能推荐
JWT(Json Web Token)实现无状态登录_无状态token登录-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读685次。1.1.什么是有状态?有状态服务,即服务端需要记录每次会话的客户端信息,从而识别客户端身份,根据用户身份进行请求的处理,典型的设计如tomcat中的session。例如登录:用户登录后,我们把登录者的信息保存在服务端session中,并且给用户一个cookie值,记录对应的session。然后下次请求,用户携带cookie值来,我们就能识别到对应session,从而找到用户的信息。缺点是什么?服务端保存大量数据,增加服务端压力 服务端保存用户状态,无法进行水平扩展 客户端请求依赖服务.._无状态token登录
SDUT OJ逆置正整数-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读293次。SDUT OnlineJudge#include<iostream>using namespace std;int main(){int a,b,c,d;cin>>a;b=a%10;c=a/10%10;d=a/100%10;int key[3];key[0]=b;key[1]=c;key[2]=d;for(int i = 0;i<3;i++){ if(key[i]!=0) { cout<<key[i.
年终奖盲区_年终奖盲区表-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.2k次。年终奖采用的平均每月的收入来评定缴税级数的,速算扣除数也按照月份计算出来,但是最终减去的也是一个月的速算扣除数。为什么这么做呢,这样的收的税更多啊,年终也是一个月的收入,凭什么减去12*速算扣除数了?这个霸道(不要脸)的说法,我们只能合理避免的这些跨级的区域了,那具体是那些区域呢?可以参考下面的表格:年终奖一列标红的一对便是盲区的上下线,发放年终奖的数额一定一定要避免这个区域,不然公司多花了钱..._年终奖盲区表
matlab 提取struct结构体中某个字段所有变量的值_matlab读取struct类型数据中的值-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读7.5k次,点赞5次,收藏19次。matlab结构体struct字段变量值提取_matlab读取struct类型数据中的值
Android fragment的用法_android reader fragment-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读4.8k次。1,什么情况下使用fragment通常用来作为一个activity的用户界面的一部分例如, 一个新闻应用可以在屏幕左侧使用一个fragment来展示一个文章的列表,然后在屏幕右侧使用另一个fragment来展示一篇文章 – 2个fragment并排显示在相同的一个activity中,并且每一个fragment拥有它自己的一套生命周期回调方法,并且处理它们自己的用户输_android reader fragment
FFT of waveIn audio signals-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.8k次。FFT of waveIn audio signalsBy Aqiruse An article on using the Fast Fourier Transform on audio signals. IntroductionThe Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) allows users to view the spectrum content of _fft of wavein audio signals
随便推点
Awesome Mac:收集的非常全面好用的Mac应用程序、软件以及工具_awesomemac-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读5.9k次。https://jaywcjlove.github.io/awesome-mac/ 这个仓库主要是收集非常好用的Mac应用程序、软件以及工具,主要面向开发者和设计师。有这个想法是因为我最近发了一篇较为火爆的涨粉儿微信公众号文章《工具武装的前端开发工程师》,于是建了这么一个仓库,持续更新作为补充,搜集更多好用的软件工具。请Star、Pull Request或者使劲搓它 issu_awesomemac
java前端技术---jquery基础详解_简介java中jquery技术-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读616次。一.jquery简介 jQuery是一个快速的,简洁的javaScript库,使用户能更方便地处理HTML documents、events、实现动画效果,并且方便地为网站提供AJAX交互 jQuery 的功能概括1、html 的元素选取2、html的元素操作3、html dom遍历和修改4、js特效和动画效果5、css操作6、html事件操作7、ajax_简介java中jquery技术
Ant Design Table换滚动条的样式_ant design ::-webkit-scrollbar-corner-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.6w次,点赞5次,收藏19次。我修改的是表格的固定列滚动而产生的滚动条引用Table的组件的css文件中加入下面的样式:.ant-table-body{ &amp;::-webkit-scrollbar { height: 5px; } &amp;::-webkit-scrollbar-thumb { border-radius: 5px; -webkit-box..._ant design ::-webkit-scrollbar-corner
javaWeb毕设分享 健身俱乐部会员管理系统【源码+论文】-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读269次。基于JSP的健身俱乐部会员管理系统项目分享:见文末!
论文开题报告怎么写?_开题报告研究难点-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.8k次,点赞2次,收藏15次。同学们,是不是又到了一年一度写开题报告的时候呀?是不是还在为不知道论文的开题报告怎么写而苦恼?Take it easy!我带着倾尽我所有开题报告写作经验总结出来的最强保姆级开题报告解说来啦,一定让你脱胎换骨,顺利拿下开题报告这个高塔,你确定还不赶快点赞收藏学起来吗?_开题报告研究难点
原生JS 与 VUE获取父级、子级、兄弟节点的方法 及一些DOM对象的获取_获取子节点的路径 vue-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读6k次,点赞4次,收藏17次。原生先获取对象var a = document.getElementById("dom");vue先添加ref <div class="" ref="divBox">获取对象let a = this.$refs.divBox获取父、子、兄弟节点方法var b = a.childNodes; 获取a的全部子节点 var c = a.parentNode; 获取a的父节点var d = a.nextSbiling; 获取a的下一个兄弟节点 var e = a.previ_获取子节点的路径 vue