【深度学习】基于PyTorch搭建ResNet18、ResNet34、ResNet50、ResNet101、ResNet152网络_resnet34 resnet101-程序员宅基地
技术标签: resnet 深度学习 pytorch resnet18 34 resnet 101 152
一、使用PyTorch搭建ResNet18网络并使用CIFAR10数据集训练测试
1. ResNet18网络结构
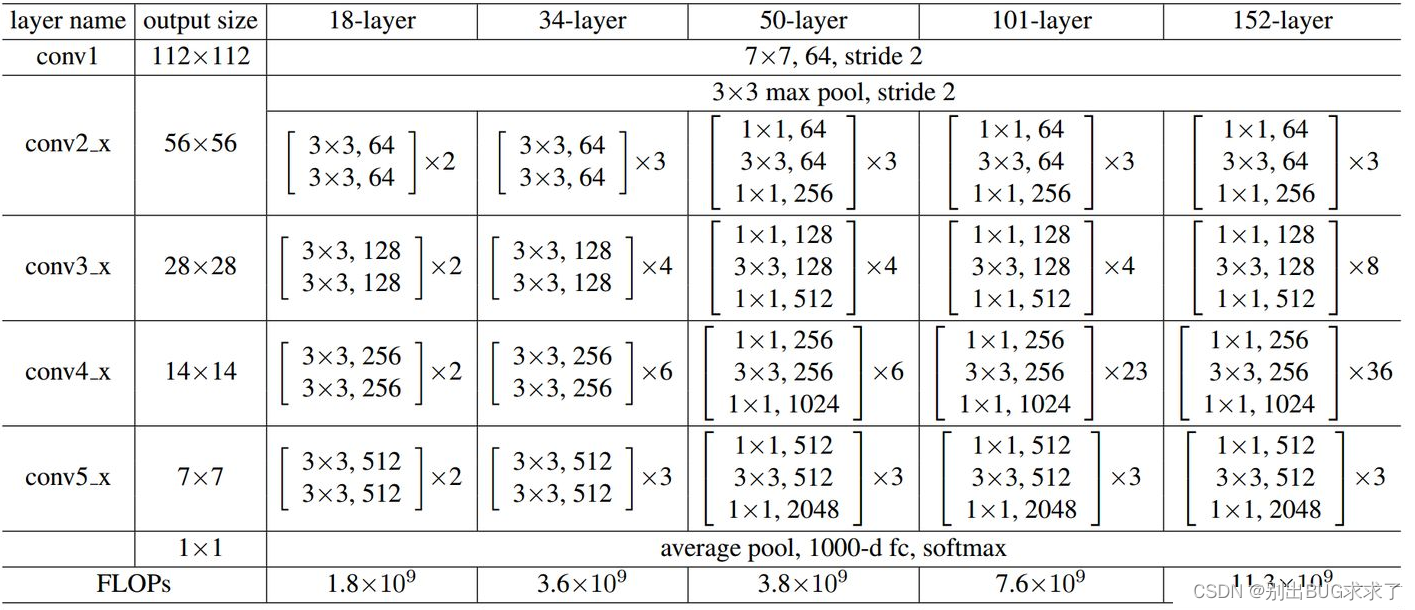
所有不同层数的ResNet:
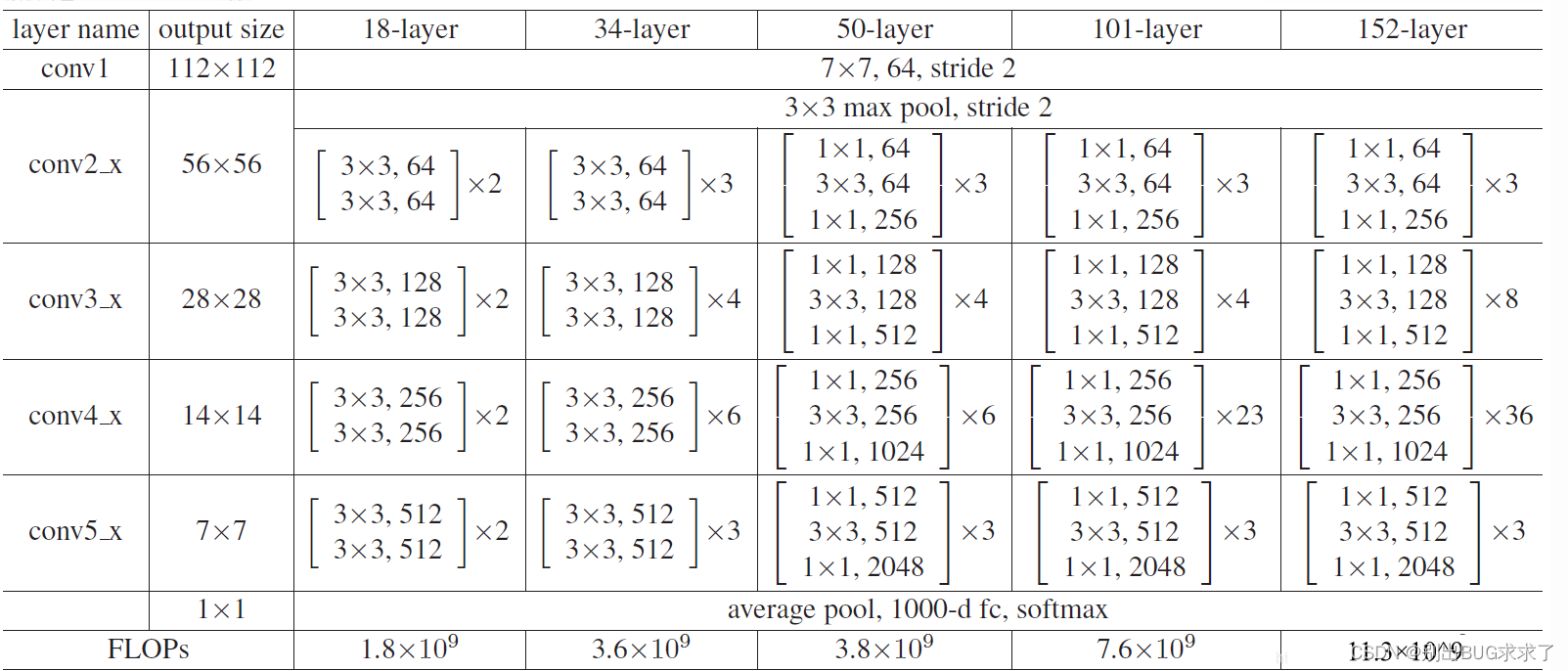
这里给出了我认为比较详细的ResNet18网络具体参数和执行流程图:
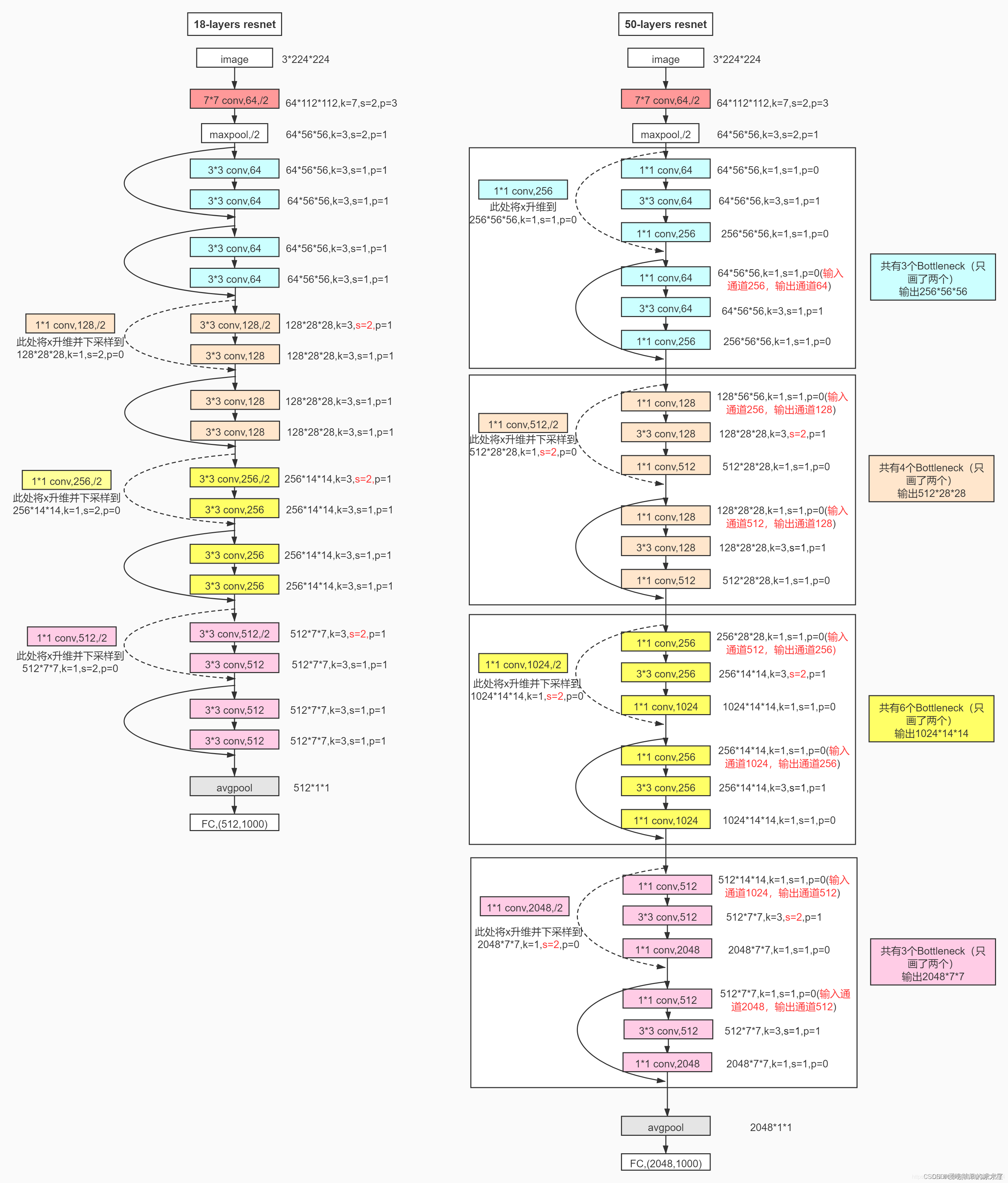
2. 实现代码
这里并未采用BasicBlock和BottleNeck复现ResNet18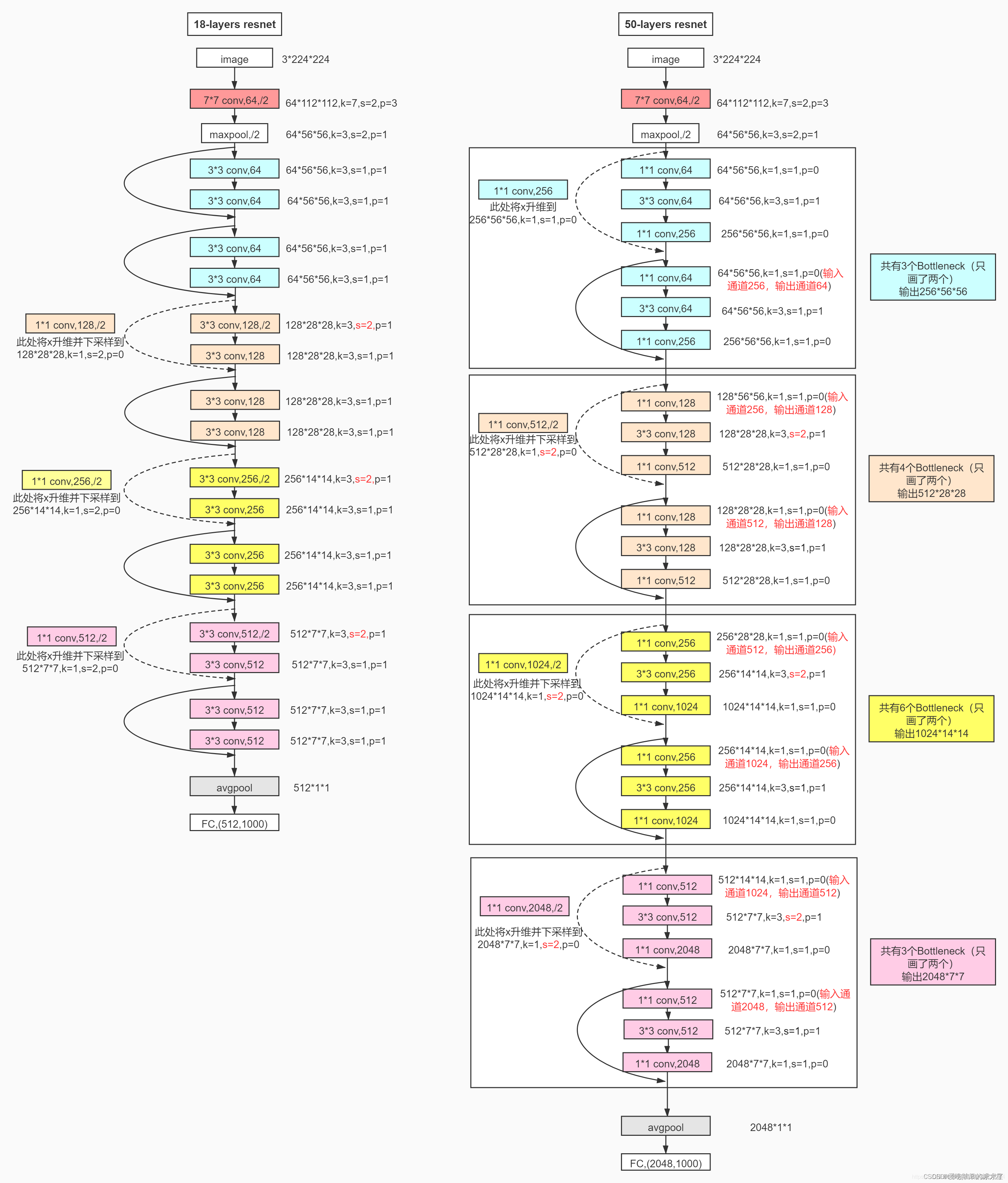
具体ResNet原理细节这里不多做描述,直接上代码
model.py网络模型部分:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
"""
把ResNet18的残差卷积单元作为一个Block,这里分为两种:一种是CommonBlock,另一种是SpecialBlock,最后由ResNet18统筹调度
其中SpecialBlock负责完成ResNet18中带有虚线(升维channel增加和下采样操作h和w减少)的Block操作
其中CommonBlock负责完成ResNet18中带有实线的直接相连相加的Block操作
注意ResNet18中所有非shortcut部分的卷积kernel_size=3, padding=1,仅仅in_channel, out_channel, stride的不同
注意ResNet18中所有shortcut部分的卷积kernel_size=1, padding=0,仅仅in_channel, out_channel, stride的不同
"""
class CommonBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride): # 普通Block简单完成两次卷积操作
super(CommonBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(out_channel, out_channel, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
def forward(self, x):
identity = x # 普通Block的shortcut为直连,不需要升维下采样
x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)), inplace=True) # 完成一次卷积
x = self.bn2(self.conv2(x)) # 第二次卷积不加relu激活函数
x += identity # 两路相加
return F.relu(x, inplace=True) # 添加激活函数输出
class SpecialBlock(nn.Module): # 特殊Block完成两次卷积操作,以及一次升维下采样
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride): # 注意这里的stride传入一个数组,shortcut和残差部分stride不同
super(SpecialBlock, self).__init__()
self.change_channel = nn.Sequential( # 负责升维下采样的卷积网络change_channel
nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size=1, stride=stride[0], padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size=3, stride=stride[0], padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(out_channel, out_channel, kernel_size=3, stride=stride[1], padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
def forward(self, x):
identity = self.change_channel(x) # 调用change_channel对输入修改,为后面相加做变换准备
x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)), inplace=True)
x = self.bn2(self.conv2(x)) # 完成残差部分的卷积
x += identity
return F.relu(x, inplace=True) # 输出卷积单元
class ResNet18(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, classes_num):
super(ResNet18, self).__init__()
self.prepare = nn.Sequential( # 所有的ResNet共有的预处理==》[batch, 64, 56, 56]
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, 7, 2, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2, 1)
)
self.layer1 = nn.Sequential( # layer1有点特别,由于输入输出的channel均是64,故两个CommonBlock
CommonBlock(64, 64, 1),
CommonBlock(64, 64, 1)
)
self.layer2 = nn.Sequential( # layer234类似,由于输入输出的channel不同,故一个SpecialBlock,一个CommonBlock
SpecialBlock(64, 128, [2, 1]),
CommonBlock(128, 128, 1)
)
self.layer3 = nn.Sequential(
SpecialBlock(128, 256, [2, 1]),
CommonBlock(256, 256, 1)
)
self.layer4 = nn.Sequential(
SpecialBlock(256, 512, [2, 1]),
CommonBlock(512, 512, 1)
)
self.pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(output_size=(1, 1)) # 卷积结束,通过一个自适应均值池化==》 [batch, 512, 1, 1]
self.fc = nn.Sequential( # 最后用于分类的全连接层,根据需要灵活变化
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(512, 256),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(256, classes_num) # 这个使用CIFAR10数据集,定为10分类
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.prepare(x) # 预处理
x = self.layer1(x) # 四个卷积单元
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
x = self.pool(x) # 池化
x = x.reshape(x.shape[0], -1) # 将x展平,输入全连接层
x = self.fc(x)
return x
train.py训练部分(使用CIFAR10数据集):
import torch
import visdom
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
from PIL import Image
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from ResNet18 import ResNet18
from torch.nn import CrossEntropyLoss
from torch import optim
BATCH_SIZE = 512 # 超参数batch大小
EPOCH = 30 # 总共训练轮数
save_path = "./CIFAR10_ResNet18.pth" # 模型权重参数保存位置
# classes = ('plane', 'car', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck') # CIFAR10数据集类别
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") # 创建GPU运算环境
print(device)
data_transform = {
# 数据预处理
"train": transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
]),
"val": transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
])
}
# 加载数据集,指定训练或测试数据,指定于处理方式
train_data = datasets.CIFAR10(root='./CIFAR10/', train=True, transform=data_transform["train"], download=True)
test_data = datasets.CIFAR10(root='./CIFAR10/', train=False, transform=data_transform["val"], download=True)
train_dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_data, BATCH_SIZE, True, num_workers=0)
test_dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_data, BATCH_SIZE, False, num_workers=0)
# # 展示图片
# x = 0
# for images, labels in train_data:
# plt.subplot(3,3,x+1)
# plt.tight_layout()
# images = images.numpy().transpose(1, 2, 0) # 把channel那一维放到最后
# plt.title(str(classes[labels]))
# plt.imshow(images)
# plt.xticks([])
# plt.yticks([])
# x += 1
# if x == 9:
# break
# plt.show()
# 创建一个visdom,将训练测试情况可视化
viz = visdom.Visdom()
# 测试函数,传入模型和数据读取接口
def evalute(model, loader):
# correct为总正确数量,total为总测试数量
correct = 0
total = len(loader.dataset)
# 取测试数据
for x, y in loader:
x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device)
# validation和test过程不需要反向传播
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
out = model(x) # 计算测试数据的输出logits
# 计算出out在第一维度上最大值对应编号,得模型的预测值
prediction = out.argmax(dim=1)
# 预测正确的数量correct
correct += torch.eq(prediction, y).float().sum().item()
# 最终返回正确率
return correct / total
net = ResNet18()
net.to(device) # 实例化网络模型并送入GPU
net.load_state_dict(torch.load(save_path)) # 使用上次训练权重接着训练
optimizer = optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.001) # 定义优化器
loss_function = CrossEntropyLoss() # 多分类问题使用交叉熵损失函数
best_acc, best_epoch = 0.0, 0 # 最好准确度,出现的轮数
global_step = 0 # 全局的step步数,用于画图
for epoch in range(EPOCH):
running_loss = 0.0 # 一次epoch的总损失
net.train() # 开始训练
for step, (images, labels) in enumerate(train_dataloader, start=0):
images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = net(images)
loss = loss_function(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
running_loss += loss.item() # 将一个epoch的损失累加
# 打印输出当前训练的进度
rate = (step + 1) / len(train_dataloader)
a = "*" * int(rate * 50)
b = "." * int((1 - rate) * 50)
print("\repoch: {} train loss: {:^3.0f}%[{}->{}]{:.3f}".format(epoch+1, int(rate * 100), a, b, loss), end="")
# 记录test的loss
viz.line([loss.item()], [global_step], win='loss', update='append')
# 每次记录之后将横轴x的值加一
global_step += 1
# 在每一个epoch结束,做一次test
if epoch % 1 == 0:
# 使用上面定义的evalute函数,测试正确率,传入测试模型net,测试数据集test_dataloader
test_acc = evalute(net, test_dataloader)
print(" epoch{} test acc:{}".format(epoch+1, test_acc))
# 根据目前epoch计算所得的acc,看看是否需要保存当前状态(即当前的各项参数值)以及迭代周期epoch作为最好情况
if test_acc > best_acc:
# 保存最好数据
best_acc = test_acc
best_epoch = epoch
# 保存最好的模型参数值状态
torch.save(net.state_dict(), save_path)
# 记录validation的val_acc
viz.line([test_acc], [global_step], win='test_acc', update='append')
print("Finish !")
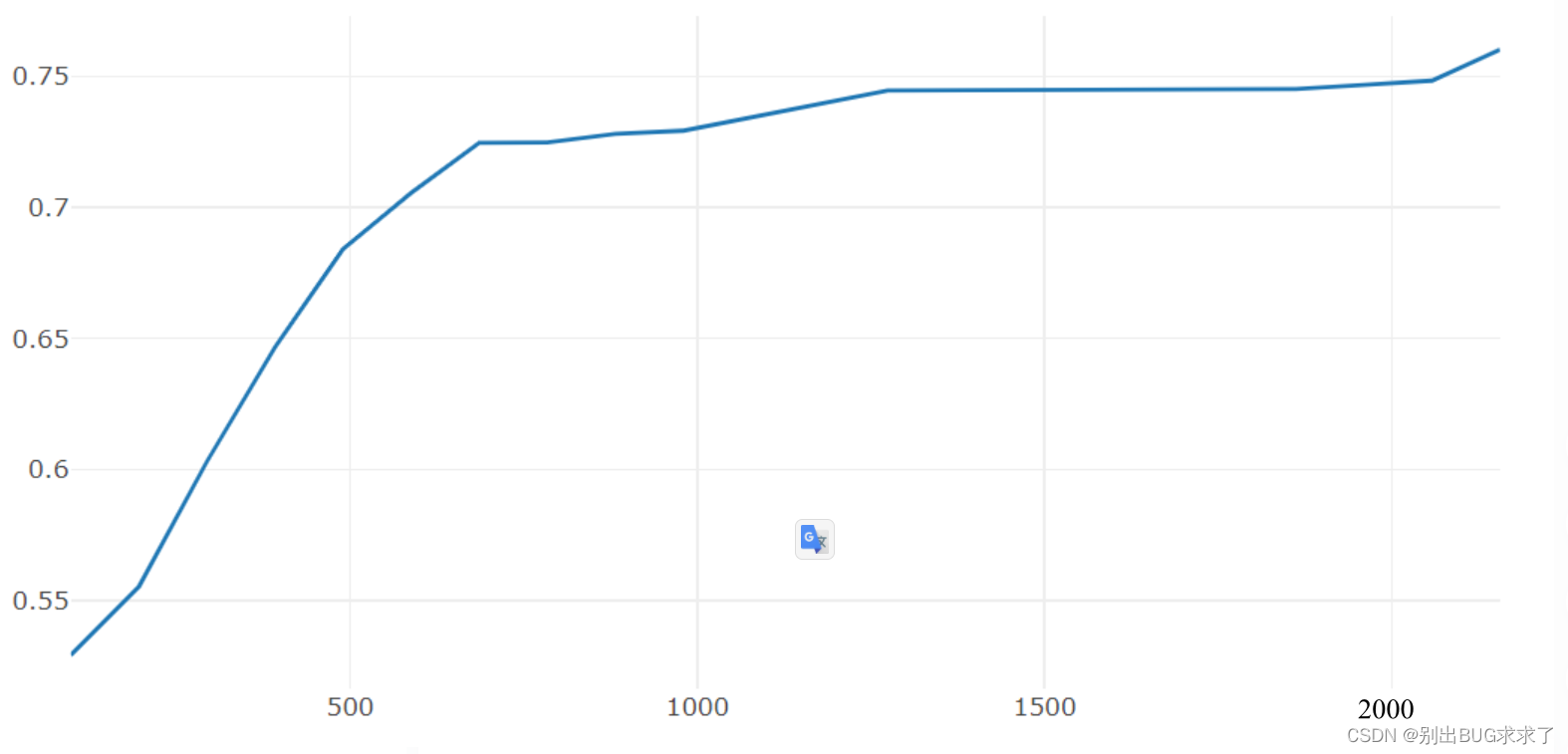
3. 训练测试结果
训练损失:
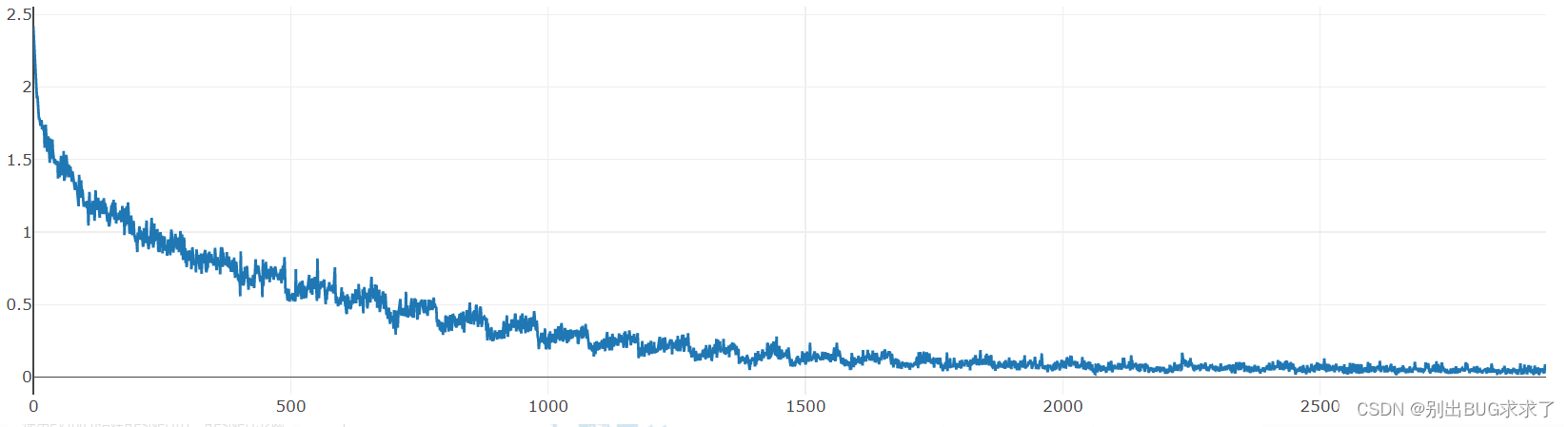
每一个epoch结束之后的测试:
训练时多次修改超参数,最后经过30次epoch之后的测试准确度达到了0.7471,没有在训练下去也没有明显提升,初学深度神经网络,第一次搭建ResNet,我的数据处理等方面处理的有一定欠缺,大家有好的建议也可以提出来
二、使用PyTorch搭建ResNet34网络
1. ResNet34网络结构
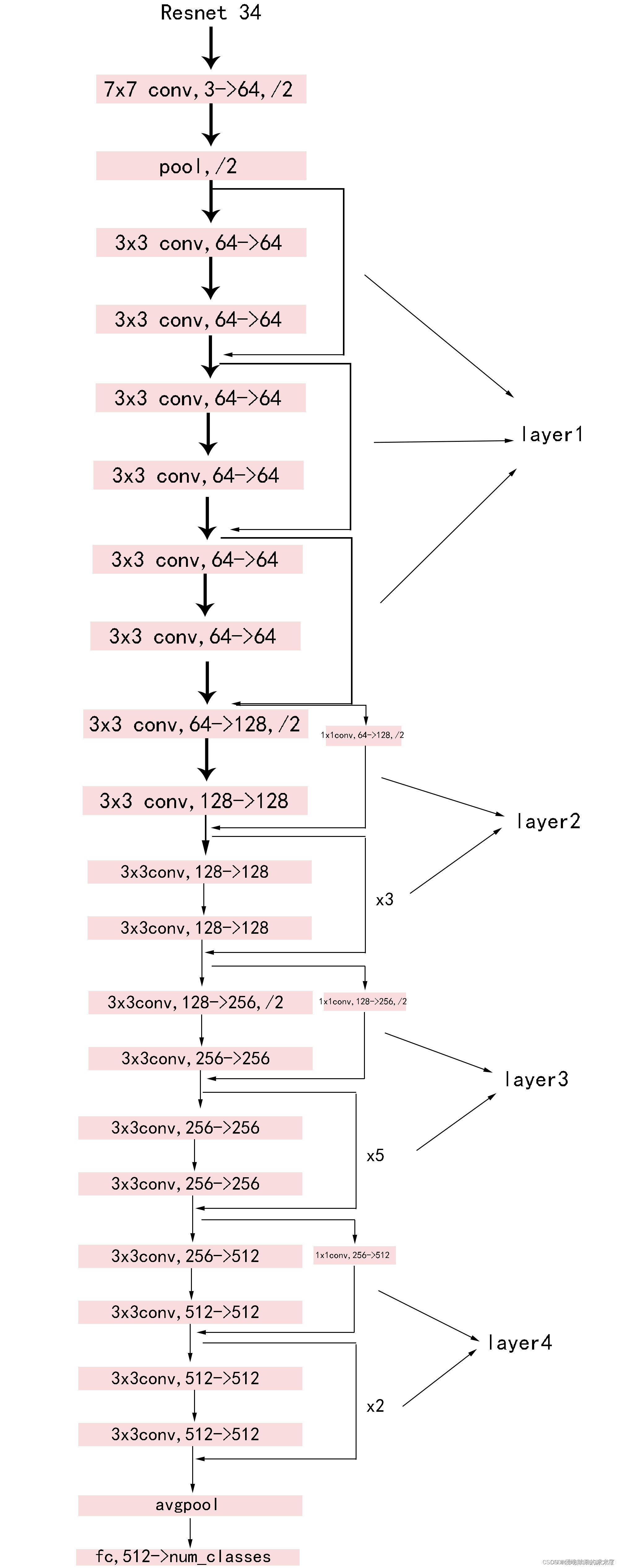
参照ResNet18的搭建,由于34层和18层几乎相同,叠加卷积单元数即可,所以没有写注释,具体可以参考我的ResNet18搭建中的注释,ResNet34的训练部分也可以参照。
2. 实现代码
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
class CommonBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride):
super(CommonBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(out_channel, out_channel, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)), inplace=True)
x = self.bn2(self.conv2(x))
x += identity
return F.relu(x, inplace=True)
class SpecialBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride):
super(SpecialBlock, self).__init__()
self.change_channel = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size=1, stride=stride[0], padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size=3, stride=stride[0], padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(out_channel, out_channel, kernel_size=3, stride=stride[1], padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
def forward(self, x):
identity = self.change_channel(x)
x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)), inplace=True)
x = self.bn2(self.conv2(x))
x += identity
return F.relu(x, inplace=True)
class ResNet34(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, classes_num):
super(ResNet34, self).__init__()
self.prepare = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, 7, 2, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2, 1)
)
self.layer1 = nn.Sequential(
CommonBlock(64, 64, 1),
CommonBlock(64, 64, 1),
CommonBlock(64, 64, 1)
)
self.layer2 = nn.Sequential(
SpecialBlock(64, 128, [2, 1]),
CommonBlock(128, 128, 1),
CommonBlock(128, 128, 1),
CommonBlock(128, 128, 1)
)
self.layer3 = nn.Sequential(
SpecialBlock(128, 256, [2, 1]),
CommonBlock(256, 256, 1),
CommonBlock(256, 256, 1),
CommonBlock(256, 256, 1),
CommonBlock(256, 256, 1),
CommonBlock(256, 256, 1)
)
self.layer4 = nn.Sequential(
SpecialBlock(256, 512, [2, 1]),
CommonBlock(512, 512, 1),
CommonBlock(512, 512, 1)
)
self.pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(output_size=(1, 1))
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(512, 256),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(256, classes_num)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.prepare(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
x = self.pool(x)
x = x.reshape(x.shape[0], -1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
三、使用PyTorch搭建ResNet50网络
看过我之前ResNet18和ResNet34搭建的朋友可能想着可不可以把搭建18和34层的方法直接用在50层以上的ResNet的搭建中,我也尝试过。但是ResNet50以上的网络搭建不像是18到34层只要简单修改卷积单元数目就可以完成,ResNet50以上的三种网络都是一个样子,只是层数不同,所以完全可以将34到50层作为一个搭建分水岭。
加上我初学PyTorch和深度神经网络,对于采用BasicBlock和BottleNeck的高效率构建还不是很懂,所以这里给出了类似前两种ResNet的简单暴力堆叠网络层的构建方法
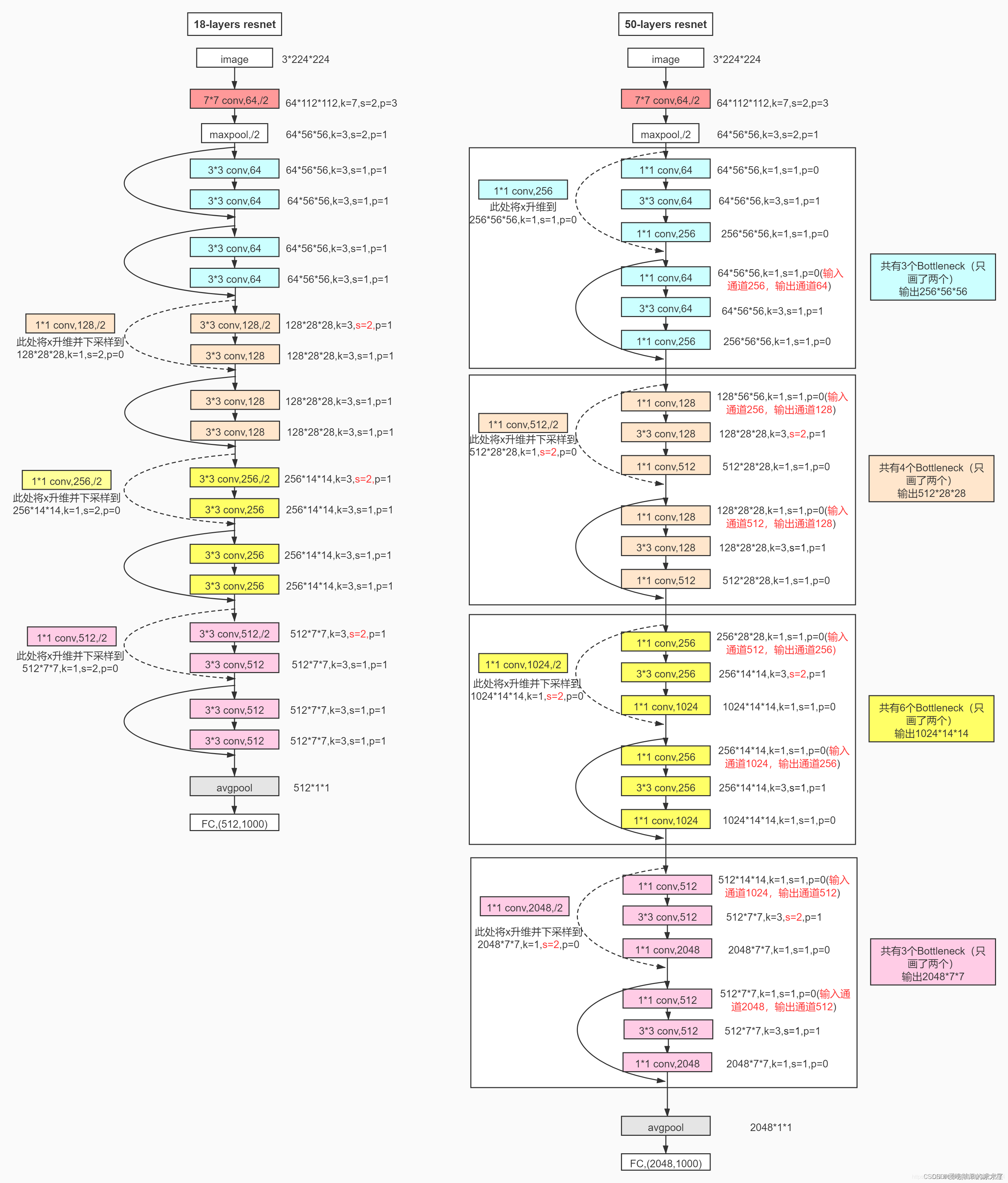
1. ResNet50网络结构
所有不同层数的ResNet:
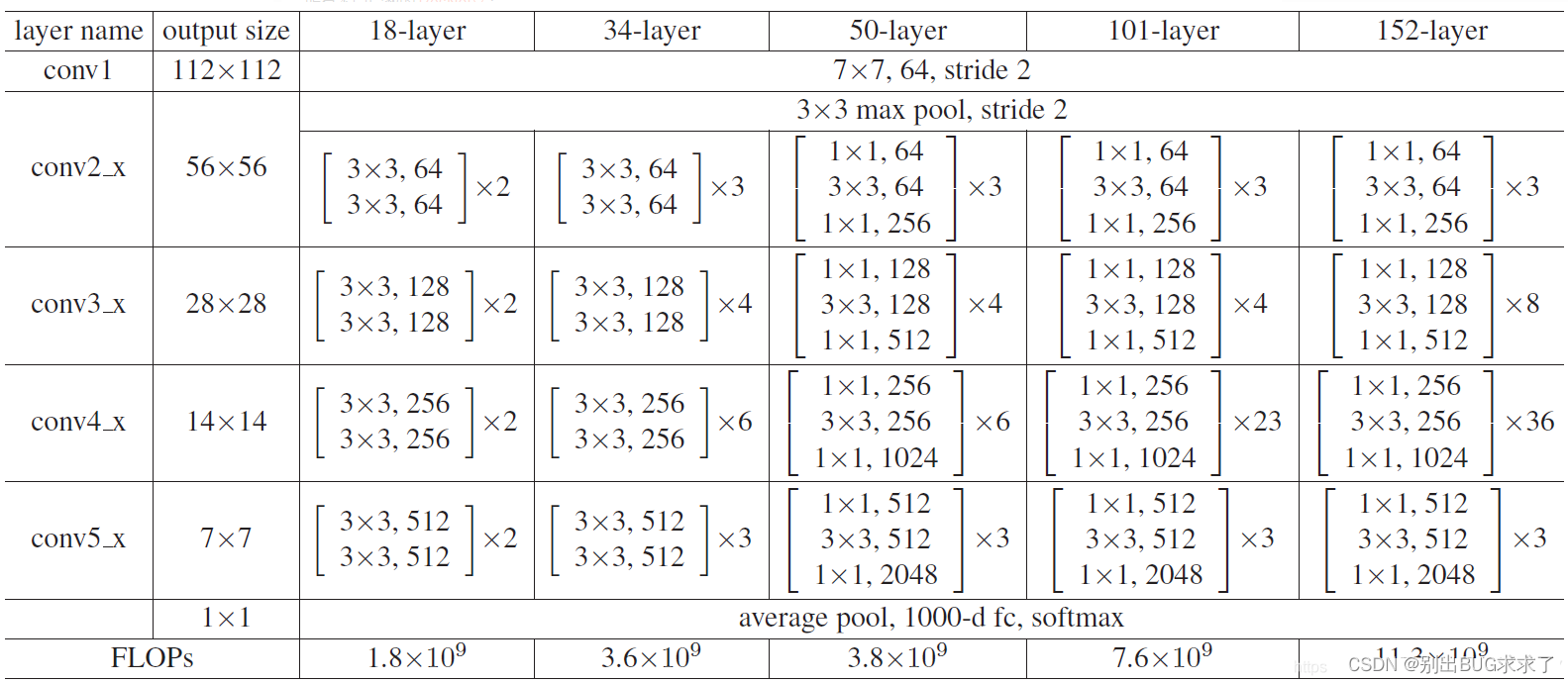
这里给出了我认为比较详细的ResNet50网络具体参数和执行流程图:
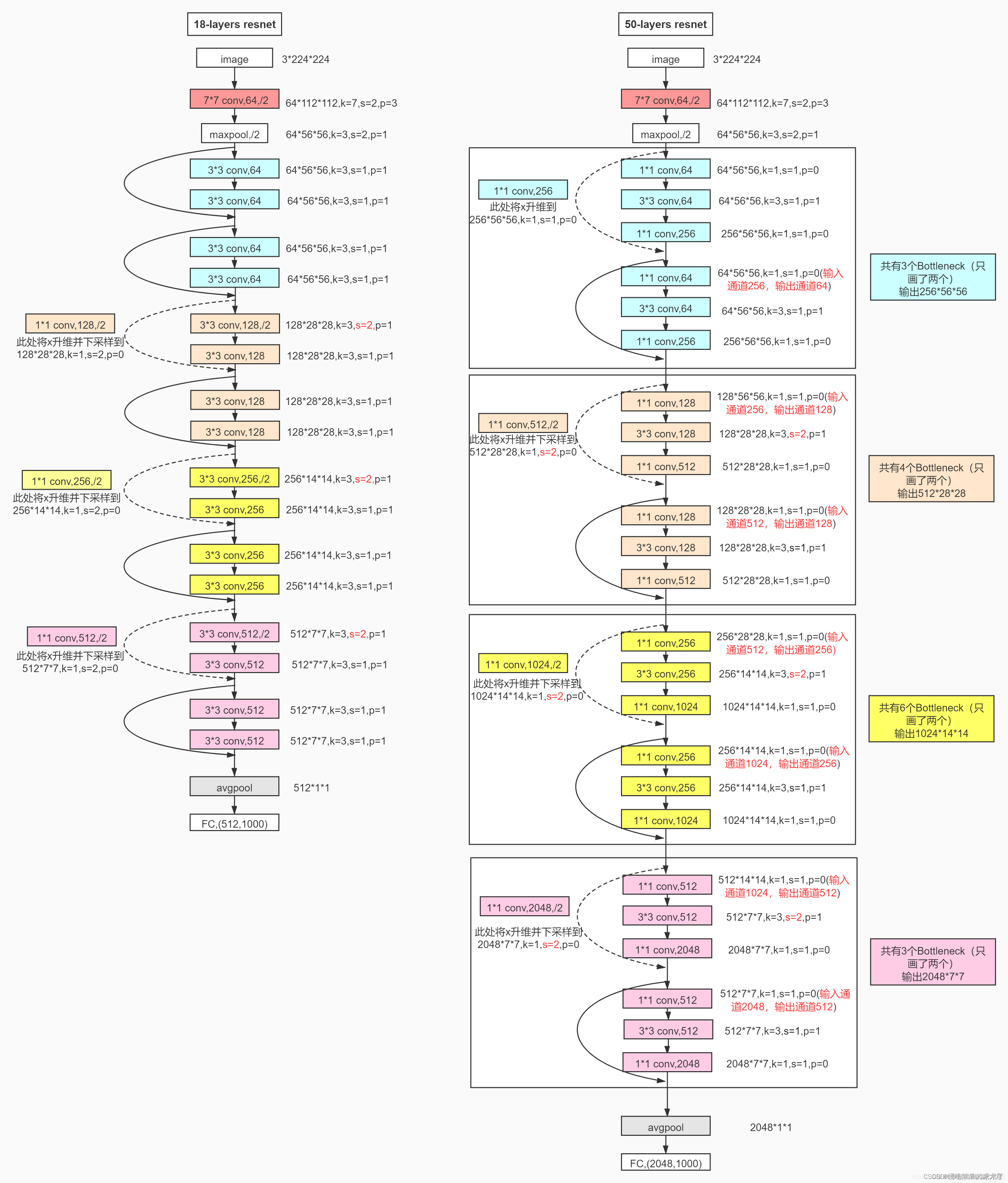
2. 实现代码
model.py模型部分:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
"""
这里的ResNet50的搭建是暴力形式,直接累加完成搭建,没采用BasicBlock和BottleNeck
第一个DownSample类,用于定义shortcut的模型函数,完成两个layer之间虚线的shortcut,负责layer1虚线的升4倍channel以及其他layer虚线的升2倍channel
观察每一个layer的虚线处升channel仅仅是升channel前后的数量不同以及stride不同,对于kernel_size和padding都分别是1和0,不作为DownSample网络类的模型参数
参数in_channel即是升之前的通道数, out_channel即是升之后的通道数, stride即是每一次升channel不同的stride步长,对于layer1升通道的stride=1,其他layer升通道的stride=2,注意不同
"""
"""
运行时一定要注意:
本网络中的ResNet50类中forward函数里面:layer1_shortcut1.to('cuda:0');layer2_shortcut1.to('cuda:0')等语句,是将实例化的DownSample
网络模型放到train.py训练脚本中定义的GPU同一环境下,不加此句一般会如下报错:
Input type (torch.cuda.FloatTensor) and weight type (torch.FloatTensor) should be the same
"""
class DownSample(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride): # 传入下采样的前后channel数以及stride步长
super(DownSample, self).__init__() # 继承父类
self.down = nn.Sequential( # 定义一个模型容器down
nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, padding=0, bias=False), # 负责虚线shortcut的唯一且重要的一次卷积
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel), # 在卷积和ReLU非线性激活之间,添加BatchNormalization
nn.ReLU(inplace=True) # shortcut最后加入一个激活函数,置inplace=True原地操作,节省内存
)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.down(x) # 前向传播函数仅仅完成down这个容器的操作
return out
"""
第一个ResNet50类,不使用BottleNeck单元完成ResNet50层以上的搭建,直接使用forward再加上前面的DownSample模型类函数,指定ResNet50所有参数构建模型
"""
class ResNet50(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, classes_num): # ResNet50仅传一个分类数目,将涉及的所有数据写死,具体数据可以参考下面的图片
super(ResNet50, self).__init__()
# 在进入layer1234之间先进行预处理,主要是一次卷积一次池化,从[batch, 3, 224, 224] => [batch, 64, 56, 56]
self.pre = nn.Sequential(
# 卷积channel从原始数据的3通道,采用64个卷积核,升到64个channel,卷积核大小、步长、padding均固定
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64), # 卷积后紧接一次BatchNormalization
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1) # 预处理最后的一次最大池化操作,数据固定
)
"""
每一个layer的操作分为使用一次的first,和使用多次的next组成,first负责每个layer的第一个单元(有虚线)的三次卷积,next负责剩下单元(直连)的三次卷积
"""
# --------------------------------------------------------------
self.layer1_first = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False), # layer1_first第一次卷积保持channel不变,和其他layer的first区别
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False), # layer1_first第二次卷积stride和其他layer_first的stride不同
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(64, 256, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False), # layer1_first第三次卷积和其他layer一样,channel升4倍
nn.BatchNorm2d(256) # 注意最后一次卷积结束不加ReLU激活函数
)
self.layer1_next = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(256, 64, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False), # layer1_next的第一次卷积负责将channel减少,减少训练参数量
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(64, 256, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False), # layer1_next的最后一次卷积负责将channel增加至可以与shortcut相加
nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
)
# -------------------------------------------------------------- # layer234操作基本相同,这里仅介绍layer2
self.layer2_first = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(256, 128, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False), # 与layer1_first第一次卷积不同,需要降channel至1/2
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, bias=False), # 注意这里的stride=2与layer34相同,与layer1区别
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(128, 512, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False), # 再次升channel
nn.BatchNorm2d(512)
)
self.layer2_next = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(512, 128, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False), # 负责循环普通的操作
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(128, 512, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512)
)
# --------------------------------------------------------------
self.layer3_first = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(512, 256, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(1024)
)
self.layer3_next = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(1024)
)
# --------------------------------------------------------------
self.layer4_first = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1024, 512, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(512, 2048, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(2048)
)
self.layer4_next = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(2048, 512, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(512, 2048, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(2048)
)
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)) # 经过最后的自适应均值池化为[batch, 2048, 1, 1]
# 定义最后的全连接层
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(p=0.5), # 以0.5的概率失活神经元
nn.Linear(2048 * 1 * 1, 1024), # 第一个全连接层
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(1024, classes_num) # 第二个全连接层,输出类结果
)
"""
forward()前向传播函数负责将ResNet类中定义的网络层复用,再与上面的DownSample类完美组合
"""
def forward(self, x):
out = self.pre(x) # 对输入预处理,输出out = [batch, 64, 56, 56]
"""
每一层layer操作由两个部分组成,第一个是带有虚线的卷积单元,其他的是循环完成普通的shortcut为直连的卷积单元
"""
layer1_shortcut1 = DownSample(64, 256, 1) # 使用DownSample实例化一个网络模型layer1_shortcut1,参数即是虚线处升channel数据,注意stride=1
layer1_shortcut1.to('cuda:0')
layer1_identity1 = layer1_shortcut1(out) # 调用layer1_shortcut1对卷积单元输入out计算虚线处的identity,用于后面与卷积单元输出相加
out = self.layer1_first(out) # 调用layer1_first完成layer1的第一个特殊的卷积单元
out = F.relu(out + layer1_identity1, inplace=True) # 将identity与卷积单元输出相加,经过relu激活函数
for i in range(2): # 使用循环完成后面几个相同输入输出相同操作的卷积单元
layer_identity = out # 直接直连identity等于输入
out = self.layer1_next(out) # 输入经过普通卷积单元
out = F.relu(out + layer_identity, inplace=True) # 两路结果相加,再经过激活函数
# --------------------------------------------------------------后面layer234都是类似的,这里仅介绍layer2
layer2_shortcut1 = DownSample(256, 512, 2) # 注意后面layer234输入输出channel不同,stride=2都是如此
layer2_shortcut1.to('cuda:0')
layer2_identity1 = layer2_shortcut1(out)
out = self.layer2_first(out)
out = F.relu(out + layer2_identity1, inplace=True) # 完成layer2的第一个卷积单元
for i in range(3): # 循环执行layer2剩下的其他卷积单元
layer_identity = out
out = self.layer2_next(out)
out = F.relu(out + layer_identity, inplace=True)
# --------------------------------------------------------------
layer3_shortcut1 = DownSample(512, 1024, 2)
layer3_shortcut1.to('cuda:0')
layer3_identity1 = layer3_shortcut1(out)
out = self.layer3_first(out)
out = F.relu(out + layer3_identity1, inplace=True)
for i in range(5):
layer_identity = out
out = self.layer3_next(out)
out = F.relu(out + layer_identity, inplace=True)
# --------------------------------------------------------------
layer4_shortcut1 = DownSample(1024, 2048, 2)
layer4_shortcut1.to('cuda:0')
layer4_identity1 = layer4_shortcut1(out)
out = self.layer4_first(out)
out = F.relu(out + layer4_identity1, inplace=True)
for i in range(2):
layer_identity = out
out = self.layer4_next(out)
out = F.relu(out + layer_identity, inplace=True)
# 最后一个全连接层
out = self.avg_pool(out) # 经过最后的自适应均值池化为[batch, 2048, 1, 1]
out = out.reshape(out.size(0), -1) # 将卷积输入[batch, 2048, 1, 1]展平为[batch, 2048*1*1]
out = self.fc(out) # 经过最后一个全连接单元,输出分类out
return out
ResNet50的训练可以参照前面ResNet18搭建中的训练和测试部分:
经过手写ResNet50网络模型的暴力搭建,我认识到了要想把ResNet及其其他复杂网络的搭建,前提必须要把模型整个流程环节全部弄清楚
例如,ResNet50里面每一次的shortcut里面的升维操作的in_channel,out_channel,kernel_size,stride,padding的参数大小变化
每一个卷积单元具体参数都是什么样的,如何才能最大化简化代码;
还有就是搭建复杂的网络模型中,一定要做到步步为营,一步步搭建并检验,每一步都要理解有理有据,最后才能将整个网络搭建起来
还有一个意外收获就是在训练过程中,发现了这样的报错:
Input type (torch.cuda.FloatTensor) and weight type (torch.FloatTensor) should be the same
原来是因为输入的数据类型为torch.cuda.FloatTensor,说明输入数据在GPU中。模型参数的数据类型为torch.FloatTensor,说明模型还在CPU
故在ResNet50的forward()函数中对实例化的DownSample网络添加到和train.py对ResNet50实例化的网络模型的同一个GPU下,解决了错误
四、使用PyTorch搭建ResNet101、ResNet152网络
参照前面ResNet50的搭建,由于50层以上几乎相同,叠加卷积单元数即可,所以没有写注释。
ResNet101和152的搭建注释可以参照我的ResNet50搭建中的注释
ResNet101和152的训练可以参照我的ResNet18搭建中的训练部分
ResNet101和152可以依旧参照ResNet50的网络图片:
1. 网络结构
2. 实现代码
(1)ResNet101的model.py模型:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
class DownSample(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride):
super(DownSample, self).__init__()
self.down = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.down(x)
return out
class ResNet101(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, classes_num): # 指定分类数
super(ResNet101, self).__init__()
self.pre = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
)
# --------------------------------------------------------------------
self.layer1_first = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(64, 256, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
)
self.layer1_next = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(256, 64, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(64, 256, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
)
# --------------------------------------------------------------------
self.layer2_first = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(256, 128, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(128, 512, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512)
)
self.layer2_next = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(512, 128, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(128, 512, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512)
)
# --------------------------------------------------------------------
self.layer3_first = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(512, 256, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(1024)
)
self.layer3_next = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(1024)
)
# --------------------------------------------------------------------
self.layer4_first = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1024, 512, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(512, 2048, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(2048)
)
self.layer4_next = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(2048, 512, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(512, 2048, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(2048)
)
# --------------------------------------------------------------------
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(2048 * 1 * 1, 1000),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(1000, classes_num)
)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.pre(x)
# --------------------------------------------------------------------
layer1_shortcut = DownSample(64, 256, 1)
layer1_shortcut.to('cuda:0')
layer1_identity = layer1_shortcut(out)
out = self.layer1_first(out)
out = F.relu(out + layer1_identity, inplace=True)
for i in range(2):
identity = out
out = self.layer1_next(out)
out = F.relu(out + identity, inplace=True)
# --------------------------------------------------------------------
layer2_shortcut = DownSample(256, 512, 2)
layer2_shortcut.to('cuda:0')
layer2_identity = layer2_shortcut(out)
out = self.layer2_first(out)
out = F.relu(out + layer2_identity, inplace=True)
for i in range(3):
identity = out
out = self.layer2_next(out)
out = F.relu(out + identity, inplace=True)
# --------------------------------------------------------------------
layer3_shortcut = DownSample(512, 1024, 2)
layer3_shortcut.to('cuda:0')
layer3_identity = layer3_shortcut(out)
out = self.layer3_first(out)
out = F.relu(out + layer3_identity, inplace=True)
for i in range(22):
identity = out
out = self.layer3_next(out)
out = F.relu(out + identity, inplace=True)
# --------------------------------------------------------------------
layer4_shortcut = DownSample(1024, 2048, 2)
layer4_shortcut.to('cuda:0')
layer4_identity = layer4_shortcut(out)
out = self.layer4_first(out)
out = F.relu(out + layer4_identity, inplace=True)
for i in range(2):
identity = out
out = self.layer4_next(out)
out = F.relu(out + identity, inplace=True)
# --------------------------------------------------------------------
out = self.avg_pool(out)
out = out.reshape(out.size(0), -1)
out = self.fc(out)
return out
(2) ResNet152的model.py模型:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
class DownSample(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride):
super(DownSample, self).__init__()
self.down = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.down(x)
return out
class ResNet152(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, classes_num): # 指定了分类数目
super(ResNet152, self).__init__()
self.pre = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
)
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------
self.layer1_first = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(64, 256, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
)
self.layer1_next = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(256, 64, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(64, 256, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
)
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------
self.layer2_first = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(256, 128, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(128, 512, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512)
)
self.layer2_next = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(512, 128, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(128, 512, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512)
)
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------
self.layer3_first = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(512, 256, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(1024)
)
self.layer3_next = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(1024)
)
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------
self.layer4_first = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1024, 512, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(512, 2048, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(2048)
)
self.layer4_next = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(2048, 512, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(512, 2048, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(2048)
)
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(2048 * 1 * 1, 1000),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(1000, classes_num)
)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.pre(x)
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------
layer1_shortcut = DownSample(64, 256, 1)
# layer1_shortcut.to('cuda:0')
layer1_identity = layer1_shortcut(out)
out = self.layer1_first(out)
out = F.relu(out + layer1_identity, inplace=True)
for i in range(2):
identity = out
out = self.layer1_next(out)
out = F.relu(out + identity, inplace=True)
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------
layer2_shortcut = DownSample(256, 512, 2)
# layer2_shortcut.to('cuda:0')
layer2_identity = layer2_shortcut(out)
out = self.layer2_first(out)
out = F.relu(out + layer2_identity, inplace=True)
for i in range(7):
identity = out
out = self.layer2_next(out)
out = F.relu(out + identity, inplace=True)
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------
layer3_shortcut = DownSample(512, 1024, 2)
# layer3_shortcut.to('cuda:0')
layer3_identity = layer3_shortcut(out)
out = self.layer3_first(out)
out = F.relu(out + layer3_identity, inplace=True)
for i in range(35):
identity = out
out = self.layer3_next(out)
out = F.relu(out + identity, inplace=True)
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------
layer4_shortcut = DownSample(1024, 2048, 2)
# layer4_shortcut.to('cuda:0')
layer4_identity = layer4_shortcut(out)
out = self.layer4_first(out)
out = F.relu(out + layer4_identity, inplace=True)
for i in range(2):
identity = out
out = self.layer4_next(out)
out = F.relu(out + identity, inplace=True)
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------
out = self.avg_pool(out)
out = out.reshape(out.size(0), -1)
out = self.fc(out)
return out
智能推荐
wap svg 第八章 文字text--上拿-理疗-脚底安磨_html中如何设置svg<text>文字大小-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.8w次,点赞3次,收藏10次。虽然它可能是真实的,每一个画面讲述了一个故事,这是完全正确的,用言语来帮助讲故事。因此,SVG有几个元素,让你将文本添加到您的图形。文本术语Text Terminology在我们调查的主要方法添加文本,的<TEXT>元素之前,我们应该定义一些术语,你会看到,如果你读了SVG规范,或者如果你的工作与文字在任何图形环境:字符一个字符,作为一个XML文档而言,是一个数..._html中如何设置svg文字大小
GreenPlum运维监控工具-gpcc-web安装_gpcc安装-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读7.3k次,点赞4次,收藏3次。Greenplum Command Center(GPCC)是由Pivotal Software推出的一款监控和管理Greenplum Database的Web应用程序。它提供了一个易于使用的界面,可以帮助管理员监控集群的性能、诊断问题、管理用户和权限、设置预警和警报,并执行其他管理任务。GPCC具有以下主要功能:监控集群性能:GPCC提供了关于Greenplum集群中各个组件的性能指标的详细信息,包括查询性能、磁盘和内存使用情况、系统负载、网络流量等。_gpcc安装
中文编程,最精致的python访客登记系统实例项目,微信机器人不再只当人工智障------07_基于python的访客管理系统-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读473次。中文编程,最精致的python访客登记系统实例项目,微信机器人不再只当人工智障------07 - 浩海泛舟的文章 - 知乎 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/51771041面向套路编程(上)泛舟n天没更新,终于把这篇琢磨出来了.在泛舟的零基础入门系列里,开篇就指明了编程就是一个 数据输入>>>方法计算>>>输出结果 ..._基于python的访客管理系统
定积分华里士公式推广_分部积分法与点火公式|第四十六回|高数(微积分)...-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.3w次,点赞17次,收藏34次。原标题:分部积分法与点火公式|第四十六回|高数(微积分)之前几次我们都在讲定积分计算的换元法,换元法对于定积分的计算确实很重要,也非常好用,因为定积分的结果是一个固定的数,所以相比于不定积分的换元法,我们最后不需要再换回去,这是多么的喜人!今天我们要来学习定积分计算的分部积分法,同样还是要记住那个五字真言“反对幂指三”,顺序靠后的和 dx 凑: 下面来看例题:例一 例二 例三 例四 例五 例六 一..._华里士公式推广到0-2π
openstack多个外部网络可能引发的网络问题_openstack路由接口down-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.9k次。在多个外部网络的环境中,如果_openstack路由接口down
ios NSString 截取汉字 数字 字母-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读232次。字符串截取:删除字符串中的字母+汉字NSString *string = @"你bushi1222真正90-快乐";NSRegularExpression *regular = [NSRegularExpression regularExpressionWithPattern:@"[a-zA-Z\u4e00-\u9fa5]+" options:0 error:NULL];resul..._ios 字符截取数字前面的字母怎么弄
随便推点
[Android]-[adb] user版本开启adb且去掉adb授权弹框_免adb授权修改-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.3k次。配置两个属性即可:1.使user版本可以adbdevice/mediatek/mt6739/device.mk ifeq ($(TARGET_BUILD_VARIANT),user)- PRODUCT_DEFAULT_PROPERTY_OVERRIDES += persist.sys.usb.config=mtp+ PRODUCT_DEFAULT_PROPERTY_OVERRIDES += persist.sys.usb.config=mtp,adb2.去掉user版本授权usb弹框b_免adb授权修改
FreeBSD软件安装卸载工具:Ports和Packages详解-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读432次。FNP:FAQ - Ports and Packages v 1.52004.08.20 Table of Contents1、如何只抓取 tarball?2、如何仅做到解开 tarball的步骤?3、如何仅做到解开 tarball 并补上官方提供的 patch?4、如何安装一个新的 port?5、如何安装一个新的 port,并将打包(package)起来?6、如何打包一个 port,并将其所有相..._linux ports
终于,狂神说SSM及SpringBoot系列文章完更!!!_狂神博客-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读10w+次,点赞1.3k次,收藏8.5k次。经过了近一个月的时间,小狂神终于将SSM及SpringBoot视频对应文章更新完毕!!!记得文末喜欢走一波,码字不易,从公众号开通,就保持日更,何尝不是一种打卡呢?你们都坚持看了吗~如果..._狂神博客
HDFS的EditLog和FsImage作用详细解析,超详细!(含部分非原创图片,大部分原创总结)_hdfs editlog-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读698次,点赞7次,收藏10次。EditLog和FsImage的概念,以及与SecondaryNameNode的关系问题,以及EditLog和FsImage的重要性问题。_hdfs editlog
JS 系列之 事件—表单事件_js input event-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.6k次。今天跟大家分享一下JS系列之表单事件。1 表单事件的种类1.1 input 事件input事件当、、的值发生变化时触发。对于复选框()或单选框(),用户改变选项时,也会触发这个事件。另外,对于打开contenteditable属性的元素,只要值发生变化,也会触发input事件。input事件的一个特点,就是会连续触发,比如用户每按下一次按键,就会触发一次input事件。input事件对象..._js input event
菜单下拉条-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读82次。最近 ,用到了一些js的知识,稍微复习了下,还把之前写的js代码又复习了一遍,这里贴上来!<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"><html xmlns="http:/..._菜单下拉条