springboot中的自动装箱原理_springboot自动装箱-程序员宅基地
技术标签: spring 详细 spring boot java 专业
引言:
大家在使用springboot的时候不得不感叹它的功能强大和方便,但是作为一个合格的程序员,单纯只是去使用框架是远远不够的!
我们知道,Spring Boot 项目创建完成后,即使不进行任何的配置,也能够顺利地运行,这都要归功于 Spring Boot 的自动化配置。
Spring Boot 默认使用 application.properties 或 application.yml 作为其全局配置文件,我们可以在该配置文件中对各种自动配置属性(server.port、logging.level.* 、spring.config.active.no-profile 等等)进行修改,并使之生效,那么您有没有想过这些属性是否有据可依呢?
而这个答案的回答是"是,肯定有据可依",当我们感叹框架功能之强大、使用之便捷之余,我们也要有深究原理的精神,任何框架的功能的强大和方便都是由一行行的代码所支撑的。
Spring Factories 实现原理
springboot的自动装箱功能的实现是基于spring factories机制所实现的。Spring Factories 机制是 Spring Boot 中的一种服务发现机制,这种扩展机制与 Java SPI 机制十分相似(而java的SPI机制这篇博客,我之前想着发表的,但是因为一些原因导致没有发表成功,在之后这段时间,我会找个时间发布,如果有不懂SPI服务的到时候可以去看一看)。Spring Boot 会自动扫描所有 Jar 包类路径下 META-INF/spring.factories 文件,并读取其中的内容,进行实例化,这种机制也是 Spring Boot Starter 的基础。
而spring factories机制的实现主要依赖一个SpringFactoriesLoader类和多个spring.factories 文件。
spring.factories
spring.factories文件和java属性文件(.properties)差不多,其中包含一组或多组键值对(key=vlaue),其中,key 的取值为接口的完全限定名;value 的取值为接口实现类的完全限定名,一个接口可以设置多个实现类,不同实现类之间使用“,”隔开,例如:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportFilter=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnBeanCondition,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnWebApplicationCondition
SpringFactoriesLoader
spring-core 包里定义了 SpringFactoriesLoader 类,这个类会扫描所有 Jar 包类路径下的 META-INF/spring.factories 文件,并获取指定接口的配置。在 SpringFactoriesLoader 类中定义了两个对外的方法,如下表。
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| loadFactories(Class factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) | 根据接口获取其实现类的实例;该方法返回的是实现类对象列表 |
| loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) | 根据接口l获取其实现类的名称;该方法返回的是实现类的类名的列表 |
以上两个方法的关键都是从指定的 ClassLoader 中获取 spring.factories 文件,并解析得到类名列表,具体代码如下:
loadFactories方法:能够获取指定接口的实现类对象
public static <T> List<T> loadFactories(Class<T> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
Assert.notNull(factoryType, "'factoryType' must not be null");
ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader;
if (classLoader == null) {
classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader();
}
List<String> factoryImplementationNames = loadFactoryNames(factoryType, classLoaderToUse);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loaded [" + factoryType.getName() + "] names: " + factoryImplementationNames);
}
List<T> result = new ArrayList(factoryImplementationNames.size());
Iterator var5 = factoryImplementationNames.iterator();
while(var5.hasNext()) {
String factoryImplementationName = (String)var5.next();
result.add(instantiateFactory(factoryImplementationName, factoryType, classLoaderToUse));
}
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(result);
return result;
}
loadFactoryNames方法:能够根据接口获取其实现类类名的集合
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader;
if (classLoader == null) {
classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader();
}
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
return (List)loadSpringFactories(classLoaderToUse).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
而在上面的loadFactoryNames方法中调用了一个内部方法loadSpringFactories方法,这个方法的作用能够读取该项目中所有 Jar 包类路径下 META-INF/spring.factories 文件的配置内容,并以 Map 集合的形式返回。
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(ClassLoader classLoader) {
Map<String, List<String>> result = (Map)cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
} else {
HashMap result = new HashMap();
try {
Enumeration urls = classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories");
while(urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator();
while(var6.hasNext()) {
Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry)var6.next();
String factoryTypeName = ((String)entry.getKey()).trim();
String[] factoryImplementationNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue());
String[] var10 = factoryImplementationNames;
int var11 = factoryImplementationNames.length;
for(int var12 = 0; var12 < var11; ++var12) {
String factoryImplementationName = var10[var12];
((List)result.computeIfAbsent(factoryTypeName, (key) -> {
return new ArrayList();
})).add(factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
result.replaceAll((factoryType, implementations) -> {
return (List)implementations.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), Collections::unmodifiableList));
});
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
} catch (IOException var14) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]", var14);
}
}
}
到此,我们就已经了解了spring factories的基本原理。下面我们再来了解自动配置的加载是如何实现的
自动配置的加载
Spring Boot 自动化配置也是基于 Spring Factories 机制实现的,在 spring-boot-autoconfigure-xxx.jar 类路径下的 META-INF/spring.factories 中设置了 Spring Boot 自动配置的内容 ,如下。
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.LifecycleAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.MessageSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.couchbase.CouchbaseAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.dao.PersistenceExceptionTranslationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ReactiveElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ReactiveElasticsearchRestClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jdbc.JdbcRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jpa.JpaRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.solr.SolrRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.r2dbc.R2dbcDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.r2dbc.R2dbcRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisReactiveAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.rest.RepositoryRestMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.web.SpringDataWebAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRestClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.gson.GsonAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.h2.H2ConsoleAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hateoas.HypermediaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastJpaDependencyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.codec.CodecsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.influx.InfluxDbAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.info.ProjectInfoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.integration.IntegrationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JndiDataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.XADataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JmsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jmx.JmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JndiConnectionFactoryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.activemq.ActiveMQAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.artemis.ArtemisAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jersey.JerseyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jooq.JooqAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jsonb.JsonbAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.kafka.KafkaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.availability.ApplicationAvailabilityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.embedded.EmbeddedLdapAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.LdapAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.liquibase.LiquibaseAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderValidatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.embedded.EmbeddedMongoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoReactiveAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.neo4j.Neo4jAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.quartz.QuartzAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.r2dbc.R2dbcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.r2dbc.R2dbcTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketRequesterAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketServerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketStrategiesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.UserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityFilterAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveSecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveUserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.rsocket.RSocketSecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.saml2.Saml2RelyingPartyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.sendgrid.SendGridAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.session.SessionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.servlet.OAuth2ClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.reactive.ReactiveOAuth2ClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.servlet.OAuth2ResourceServerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.reactive.ReactiveOAuth2ResourceServerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.solr.SolrAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskSchedulingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.jta.JtaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.validation.ValidationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.client.RestTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.embedded.EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.ReactiveWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.WebFluxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.error.ErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.ClientHttpConnectorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.WebClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.reactive.WebSocketReactiveAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketServletAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.WebServicesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.client.WebServiceTemplateAutoConfiguration
以上配置中,value 取值是由多个 xxxAutoConfiguration (使用逗号分隔)组成,每个 xxxAutoConfiguration 都是一个自动配置类。Spring Boot 启动时,会利用 Spring-Factories 机制,将这些 xxxAutoConfiguration 实例化并作为组件加入到容器中,以实现 Spring Boot 的自动配置。
@EnableAutoConfiguration注解
@EnableAutoConfiguration 注解用于开启 Spring Boot 的自动配置功能, 它使用 Spring 框架提供的 @Import 注解通过 AutoConfigurationImportSelector类(选择器)给容器中导入自动配置组件。而这个注解是SpringBootApplication的元注解之一。
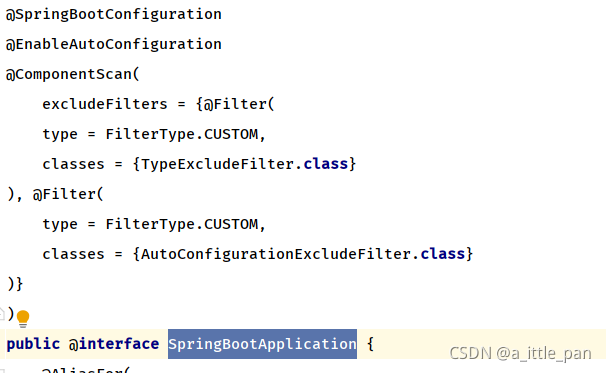
而这个能够帮助SpringBootApplication这个注解实现自动装配的功能,当然,SpringBootApplication这个注解不单纯只有这一个功能,本文不对其他功能进行一个解释,再提一嘴SpringBootApplication注解的功能主要都是由它的元注解所完成。
好了,回到正题,我们知道SpringBootApplication的自动配置功能是由EnableAutoConfiguration 注解所实现的,我们现在就去看看这个注解
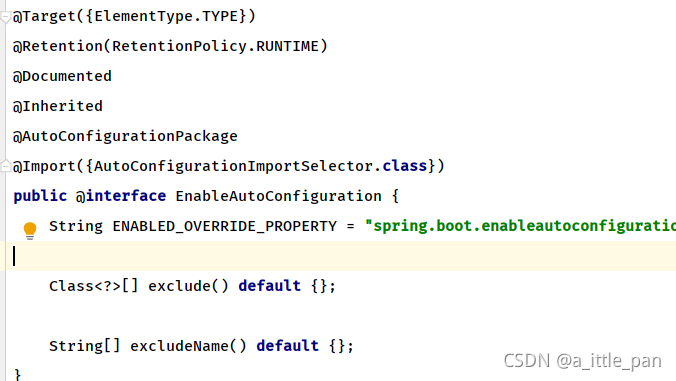
在这个注解中我们需要关注其中的Import元注解,它导入了一个AutoConfigurationImportSelector配置类,这个配置类会帮我们的EnableAutoConfiguration 注解完成自动配置功能。
AutoConfigurationImportSelector
AutoConfigurationImportSelector 类实现了 DeferredImportSelector 接口,AutoConfigurationImportSelector 中还包含一个静态内部类 AutoConfigurationGroup,它实现了 DeferredImportSelector 接口的内部接口 Group(Spring 5 新增)
在这个类中,我们需要重点关注三个方法:
- getImportGroup():该方法获取实现了 Group 接口的类,并实例化
- process(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata, DeferredImportSelector deferredImportSelector):该方法用于引入自动配置的集合
- selectImports():遍历自动配置类集合(Entry 类型的集合),并逐个解析集合中的配置类
他们的执行顺序是:getImportGroup—>process—>selectImports
下面我们将分别对以上 3 个方法及其调用过程进行介绍。
1.getImportGroup
AutoConfigurationImportSelector 类中 getImportGroup() 方法主要用于获取实现了 DeferredImportSelector.Group 接口的类,代码如下
public Class<? extends Group> getImportGroup() {
return AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationGroup.class;
}
2.process
静态内部类 AutoConfigurationGroup 中的核心方法是 process(),该方法通过调用 getAutoConfigurationEntry() 方法读取 spring.factories 文件中的内容,获得自动配置类的集合,代码如下
public void process(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata, DeferredImportSelector deferredImportSelector) {
Assert.state(deferredImportSelector instanceof AutoConfigurationImportSelector, () -> {
return String.format("Only %s implementations are supported, got %s", AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class.getSimpleName(), deferredImportSelector.getClass().getName());
});
AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = ((AutoConfigurationImportSelector)deferredImportSelector).getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata);
this.autoConfigurationEntries.add(autoConfigurationEntry);
Iterator var4 = autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations().iterator();
while(var4.hasNext()) {
String importClassName = (String)var4.next();
this.entries.putIfAbsent(importClassName, annotationMetadata);
}
}
getAutoConfigurationEntry() 方法通过调用 getCandidateConfigurations() 方法来获取自动配置类的完全限定名,并在经过排除、过滤等处理后,将其缓存到成员变量中,具体代码如下。
protected AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!this.isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
} else {
AnnotationAttributes attributes = this.getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
List<String> configurations = this.getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
configurations = this.removeDuplicates(configurations);
Set<String> exclusions = this.getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
this.checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = this.getConfigurationClassFilter().filter(configurations);
this.fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return new AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
}
}
在 getCandidateConfigurations() 方法中,根据 Spring Factories 机制调用 SpringFactoriesLoader 的 loadFactoryNames() 方法,根据 EnableAutoConfiguration.class (自动配置接口)获取其实现类(自动配置类)的类名的集合
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
protected Class<?> getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass() {
return EnableAutoConfiguration.class;
}
3.selectImports
以上所有方法执行完成后,selectImports() 会将 process() 方法处理后得到的自动配置类,进行过滤、排除,最后将所有自动配置类添加到容器中
public Iterable<Entry> selectImports() {
if (this.autoConfigurationEntries.isEmpty()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
} else {
Set<String> allExclusions = (Set)this.autoConfigurationEntries.stream().map(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry::getExclusions).flatMap(Collection::stream).collect(Collectors.toSet());
Set<String> processedConfigurations = (Set)this.autoConfigurationEntries.stream().map(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry::getConfigurations).flatMap(Collection::stream).collect(Collectors.toCollection(LinkedHashSet::new));
processedConfigurations.removeAll(allExclusions);
return (Iterable)this.sortAutoConfigurations(processedConfigurations, this.getAutoConfigurationMetadata()).stream().map((importClassName) -> {
return new Entry((AnnotationMetadata)this.entries.get(importClassName), importClassName);
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}
好了,到此,我们的springboot的自动装箱原理就已经讲解完毕,如果觉得有收获的话,就给博主点点赞吧(o( ̄︶ ̄)o)。
智能推荐
艾美捷Epigentek DNA样品的超声能量处理方案-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读15次。空化气泡的大小和相应的空化能量可以通过调整完全标度的振幅水平来操纵和数字控制。通过强调超声技术中的更高通量处理和防止样品污染,Epigentek EpiSonic超声仪可以轻松集成到现有的实验室工作流程中,并且特别适合与表观遗传学和下一代应用的兼容性。Epigentek的EpiSonic已成为一种有效的剪切设备,用于在染色质免疫沉淀技术中制备染色质样品,以及用于下一代测序平台的DNA文库制备。该装置的经济性及其多重样品的能力使其成为每个实验室拥有的经济高效的工具,而不仅仅是核心设施。
11、合宙Air模块Luat开发:通过http协议获取天气信息_合宙获取天气-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读4.2k次,点赞3次,收藏14次。目录点击这里查看所有博文 本系列博客,理论上适用于合宙的Air202、Air268、Air720x、Air720S以及最近发布的Air720U(我还没拿到样机,应该也能支持)。 先不管支不支持,如果你用的是合宙的模块,那都不妨一试,也许会有意外收获。 我使用的是Air720SL模块,如果在其他模块上不能用,那就是底层core固件暂时还没有支持,这里的代码是没有问题的。例程仅供参考!..._合宙获取天气
EasyMesh和802.11s对比-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读7.7k次,点赞2次,收藏41次。1 关于meshMesh的意思是网状物,以前读书的时候,在自动化领域有传感器自组网,zigbee、蓝牙等无线方式实现各个网络节点消息通信,通过各种算法,保证整个网络中所有节点信息能经过多跳最终传递到目的地,用于数据采集。十多年过去了,在无线路由器领域又把这个mesh概念翻炒了一下,各大品牌都推出了mesh路由器,大多数是3个为一组,实现在面积较大的住宅里,增强wifi覆盖范围,智能在多热点之间切换,提升上网体验。因为节点基本上在3个以内,所以mesh的算法不必太复杂,组网形式比较简单。各厂家都自定义了组_802.11s
线程的几种状态_线程状态-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读5.2k次,点赞8次,收藏21次。线程的几种状态_线程状态
stack的常见用法详解_stack函数用法-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读4.2w次,点赞124次,收藏688次。stack翻译为栈,是STL中实现的一个后进先出的容器。要使用 stack,应先添加头文件include<stack>,并在头文件下面加上“ using namespacestd;"1. stack的定义其定义的写法和其他STL容器相同, typename可以任意基本数据类型或容器:stack<typename> name;2. stack容器内元素的访问..._stack函数用法
2018.11.16javascript课上随笔(DOM)-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读71次。<li> <a href = "“#”>-</a></li><li>子节点:文本节点(回车),元素节点,文本节点。不同节点树: 节点(各种类型节点)childNodes:返回子节点的所有子节点的集合,包含任何类型、元素节点(元素类型节点):child。node.getAttribute(at...
随便推点
layui.extend的一点知识 第三方模块base 路径_layui extend-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读3.4k次。//config的设置是全局的layui.config({ base: '/res/js/' //假设这是你存放拓展模块的根目录}).extend({ //设定模块别名 mymod: 'mymod' //如果 mymod.js 是在根目录,也可以不用设定别名 ,mod1: 'admin/mod1' //相对于上述 base 目录的子目录}); //你也可以忽略 base 设定的根目录,直接在 extend 指定路径(主要:该功能为 layui 2.2.0 新增)layui.exten_layui extend
5G云计算:5G网络的分层思想_5g分层结构-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读3.2k次,点赞6次,收藏13次。分层思想分层思想分层思想-1分层思想-2分层思想-2OSI七层参考模型物理层和数据链路层物理层数据链路层网络层传输层会话层表示层应用层OSI七层模型的分层结构TCP/IP协议族的组成数据封装过程数据解封装过程PDU设备与层的对应关系各层通信分层思想分层思想-1在现实生活种,我们在喝牛奶时,未必了解他的生产过程,我们所接触的或许只是从超时购买牛奶。分层思想-2平时我们在网络时也未必知道数据的传输过程我们的所考虑的就是可以传就可以,不用管他时怎么传输的分层思想-2将复杂的流程分解为几个功能_5g分层结构
基于二值化图像转GCode的单向扫描实现-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读191次。在激光雕刻中,单向扫描(Unidirectional Scanning)是一种雕刻技术,其中激光头只在一个方向上移动,而不是来回移动。这种移动方式主要应用于通过激光逐行扫描图像表面的过程。具体而言,单向扫描的过程通常包括以下步骤:横向移动(X轴): 激光头沿X轴方向移动到图像的一侧。纵向移动(Y轴): 激光头沿Y轴方向开始逐行移动,刻蚀图像表面。这一过程是单向的,即在每一行上激光头只在一个方向上移动。返回横向移动: 一旦一行完成,激光头返回到图像的一侧,准备进行下一行的刻蚀。
算法随笔:强连通分量-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读577次。强连通:在有向图G中,如果两个点u和v是互相可达的,即从u出发可以到达v,从v出发也可以到达u,则成u和v是强连通的。强连通分量:如果一个有向图G不是强连通图,那么可以把它分成躲个子图,其中每个子图的内部是强连通的,而且这些子图已经扩展到最大,不能与子图外的任一点强连通,成这样的一个“极大连通”子图是G的一个强连通分量(SCC)。强连通分量的一些性质:(1)一个点必须有出度和入度,才会与其他点强连通。(2)把一个SCC从图中挖掉,不影响其他点的强连通性。_强连通分量
Django(2)|templates模板+静态资源目录static_django templates-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读3.9k次,点赞5次,收藏18次。在做web开发,要给用户提供一个页面,页面包括静态页面+数据,两者结合起来就是完整的可视化的页面,django的模板系统支持这种功能,首先需要写一个静态页面,然后通过python的模板语法将数据渲染上去。1.创建一个templates目录2.配置。_django templates
linux下的GPU测试软件,Ubuntu等Linux系统显卡性能测试软件 Unigine 3D-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.7k次。Ubuntu等Linux系统显卡性能测试软件 Unigine 3DUbuntu Intel显卡驱动安装,请参考:ATI和NVIDIA显卡请在软件和更新中的附加驱动中安装。 这里推荐: 运行后,F9就可评分,已测试显卡有K2000 2GB 900+分,GT330m 1GB 340+ 分,GT620 1GB 340+ 分,四代i5核显340+ 分,还有写博客的小盒子100+ 分。relaybot@re...