java-springmvc 01
技术标签: spring java-spring源码
springmvc也是在spring framework中的,不是一个单独的项目
MVC就是和Tomcat有关。
01.MVC启动的第一步,启动Tomcat(这个和springboot的run方法启动Tomcat有关)
02.SpringMVC中,最为核心的就是DispatcherServlet,在启动Tomcat的过程中:
- Tomcat会先创建DispatcherServlet对象(这一步在手写springboot框架中已经写到,Tomcat在启动的时候会启动DispatcherServlet)
- 然后调用DispatcherServlet对象的init()------这一步是用来创建spring容器
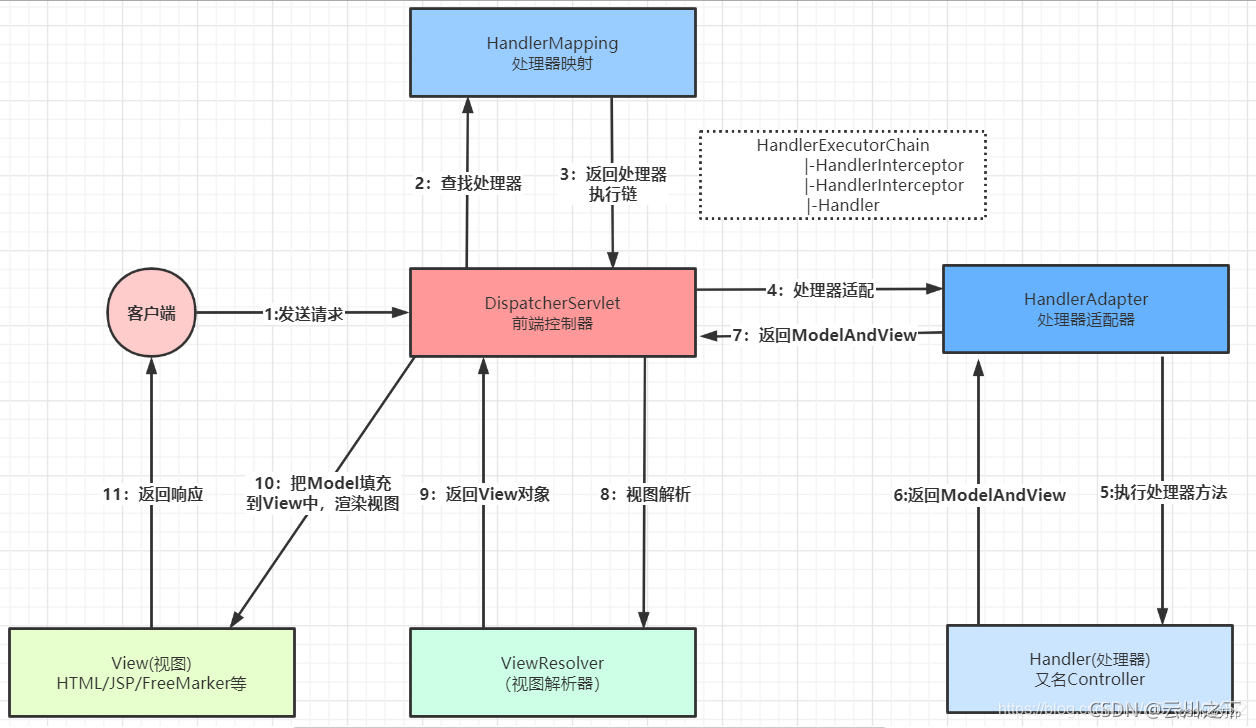
DispatcherServlet对象的init()
01.DispatcherServlet类的init()
DispatcherServlet本身默认是没有重写init()方法的
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
//DispatcherServlet中没有init方法,在父类中找
}
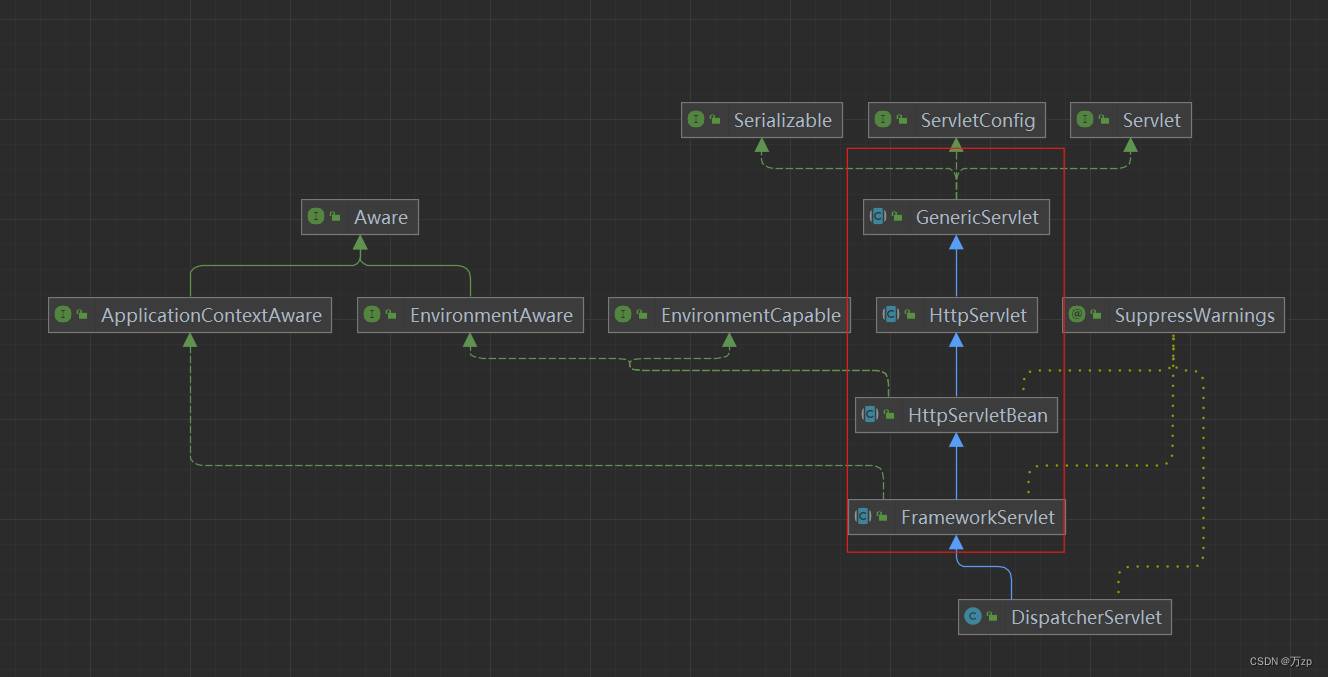
DispatcherServlet的父类HttpServletBean类init方法:
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// 解析 init-param 并封装只 pvs 中(xml)
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
// 将当前的这个 Servlet 类转化为一个 BeanWrapper,从而能够以 Spring 的方法来对 init-param 的值进行注入
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
// 属性注入
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
// 初始化Servlet,创建Spring容器
initServletBean();
}
02.DispatcherServlet的父类FrameworkServlet类
有一个属性XmlWebApplicationContext,这个是可以继承的,这代表DispatcherServlet也有这个属性
@Nullable
private WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext;
XmlWebApplicationContext是一种spring容器,这代表DispatcherServlet有一个spring容器
03.HttpServletBean的init方法 的initServletBean方法:初始化Servlet,创建Spring容器
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Initializing Servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
// 空方法,无实现·
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String value = this.enableLoggingRequestDetails ?
"shown which may lead to unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data" :
"masked to prevent unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data";
logger.debug("enableLoggingRequestDetails='" + this.enableLoggingRequestDetails +
"': request parameters and headers will be " + value);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Completed initialization in " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + " ms");
}
}
04.initServletBean方法的initWebApplicationContext方法:初始化spring容器
这里暂时不考虑父子容器,直接看 createWebApplicationContext方法
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
// 获得ContextLoaderListener存的父容器
WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// 获得子容器
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// 如果没有设置父容器 spring doGetBean
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
// 配置并且加载子容器
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// 从servlet上下文根据<contextAttribute>名字从域里面获取
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// xml会在这里创建
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
//refreshEventReceived 它会在容器加载完设置为true (通过事件onApplicationEvent)
// springboot在这初始化组件
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// 将当前容器放到servlet域中, 可以再创建子容器
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}
05.initWebApplicationContext方法的createWebApplicationContext方法:创建容器 (重点)
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass();
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext");
}
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
wac.setParent(parent);
String configLocation = getContextConfigLocation();
if (configLocation != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocation);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
}
其中的getContextClass方法:获取spring容器class对象
public Class<?> getContextClass() {
return this.contextClass;
}
this.contextClass:
private Class<?> contextClass = DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS;
public static final Class<?> DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS = XmlWebApplicationContext.class;
BeanUtils.instantiateClass:真正创建spring容器
public static <T> T instantiateClass(Class<T> clazz) throws BeanInstantiationException {
Assert.notNull(clazz, "Class must not be null");
if (clazz.isInterface()) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "Specified class is an interface");
}
try {
return instantiateClass(clazz.getDeclaredConstructor());
}
catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
Constructor<T> ctor = findPrimaryConstructor(clazz);
if (ctor != null) {
return instantiateClass(ctor);
}
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "No default constructor found", ex);
}
catch (LinkageError err) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "Unresolvable class definition", err);
}
}
此时获取 createWebApplicationContext方法 的wac
06.createWebApplicationContext方法中的getContextConfigLocation方法,获取spring容器配置类的地址
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
wac.setParent(parent);
String configLocation = getContextConfigLocation();
if (configLocation != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocation);
}
@Nullable
public String getContextConfigLocation() {
return this.contextConfigLocation;
}
用到的变量:
@Nullable
private String contextConfigLocation;
这个一般就是在web.xml文件中写好了:这个web.xml文件自动开机扫描
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>app</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>app</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/app/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
这一段就表明文件是WEB-INF文件下的spring.xml
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
spring.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"
>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zhouyu"/>
</beans>
这一段就会表面 spring容器的扫描器会扫描com.zhou这个包
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zhouyu"/>
07.getContextConfigLocation方法执行完了后,createWebApplicationContext方法会在内部顺序继续执行configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext方法:完成所有bean的解析、加载和初始化。
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// 设置id
if (this.contextId != null) {
wac.setId(this.contextId);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(getServletContext().getContextPath()) + '/' + getServletName());
}
}
// 设置servlet上下文
wac.setServletContext(getServletContext());
wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig());
wac.setNamespace(getNamespace());
// 监听器 委托设计模式
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
// 将init-param设置到Environment中
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(getServletContext(), getServletConfig());
}
// 空方法可扩展
postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac);
// 容器启动前初始化
applyInitializers(wac);
wac.refresh();
}
完成后的情况:
这一块:
// 监听器 委托设计模式
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
new ContextRefreshListener() :内部类
private class ContextRefreshListener implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {
//对ContextRefreshedEvent监听
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
FrameworkServlet.this.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
}
08.onApplicationEvent方法:spring的事件机制
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
this.refreshEventReceived = true;
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
onRefresh(event.getApplicationContext());
}
}
09.onRefresh方法:这个方法在DispatcherServlet类上的
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
10.initStrategies方法:初始化
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
11.其中
initHandlerMappings(context) 初始化HandlerMappings
initHandlerAdapters(context) 初始化HandlerAdapters
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
12.什么是Handler
Handler表示请求处理器,在SpringMVC中有四种Handler:
- 实现了Controller接口的Bean对象
- 实现了HttpRequestHandler接口的Bean对象
- 添加了@RequestMapping注解的方法
- 一个HandlerFunction对象
比如实现了Controller接口的Bean对象:
@Component("/test")
public class ZhouyuBeanNameController implements Controller {
@Override
public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
System.out.println("zhouyu");
return new ModelAndView();
}
}
实现了HttpRequestHandler接口的Bean对象:
@Component("/test")
public class ZhouyuBeanNameController implements HttpRequestHandler {
@Override
public void handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("zhouyu");
}
}
添加了@RequestMapping注解的方法:
@RequestMapping
@Component
public class ZhouyuController {
@Autowired
private ZhouyuService zhouyuService;
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, path = "/test")
@ResponseBody
public String test(String username) {
return "zhouyu";
}
}
一个HandlerFunction对象(以下代码中有两个):
@ComponentScan("com.zhouyu")
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public RouterFunction<ServerResponse> person() {
return route()
.GET("/app/person", request -> ServerResponse.status(HttpStatus.OK).body("Hello GET"))
.POST("/app/person", request -> ServerResponse.status(HttpStatus.OK).body("Hello POST"))
.build();
}
}
13.什么是HandlerMapping?
HandlerMapping负责去寻找Handler,并且保存路径和Handler之间的映射关系。HandlerMapping结构是:<path,Handler> ,实际上是由两个map联合组成 ,一个map是多值map(用来辨别get,post这些方法的,虽然url一样,但是方法不同),一个是普通map(多值map的值会作为这个map的key,value是Handler)
因为有不同类型的Handler,所以在SpringMVC中会由不同的HandlerMapping来负责寻找存储Handler,比如:
- BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping:负责Controller接口和HttpRequestHandler接口
- RequestMappingHandlerMapping:负责@RequestMapping的方法
- RouterFunctionMapping:负责RouterFunction以及其中的HandlerFunction
首先要创建HandlerMapping,用initHandlerMappings方法
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null;
// 根据类型(多个) 默认true
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
// 容器中有HandlerMapping,用HandlerMapping
Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
// We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order.
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
// 根据名字(唯一)
else {
try {
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later.
}
}
// 如果没有配HandlerMapping , 就去DispatcherServlet.properties拿默认的
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No HandlerMappings declared for servlet '" + getServletName() +
"': using default strategies from DispatcherServlet.properties");
}
}
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
if (mapping.usesPathPatterns()) {
this.parseRequestPath = true;
break;
}
}
}
getDefaultStrategies方法:默认配置HandlerMappings
private static final String DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH = "DispatcherServlet.properties";
protected <T> List<T> getDefaultStrategies(ApplicationContext context, Class<T> strategyInterface) {
if (defaultStrategies == null) {
try {
// 通过PropertiesLoaderUtils工具类加载DispatcherServlet.properties
// resource 是DispatcherServlet.properties 文件对象
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, DispatcherServlet.class);
defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load '" + DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH + "': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
String key = strategyInterface.getName();
String value = defaultStrategies.getProperty(key);
if (value != null) {
String[] classNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(value);
List<T> strategies = new ArrayList<>(classNames.length);
for (String className : classNames) {
try {
//创建DispatcherServlet.properties 文件中的类的bean
Class<?> clazz = ClassUtils.forName(className, DispatcherServlet.class.getClassLoader());
Object strategy = createDefaultStrategy(context, clazz);
strategies.add((T) strategy);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException(
"Could not find DispatcherServlet's default strategy class [" + className +
"] for interface [" + key + "]", ex);
}
catch (LinkageError err) {
throw new BeanInitializationException(
"Unresolvable class definition for DispatcherServlet's default strategy class [" +
className + "] for interface [" + key + "]", err);
}
}
return strategies;
}
else {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
}
其中DispatcherServlet.properties文件:HandlerMapping有三个实现类
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.function.support.RouterFunctionMapping
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.function.support.HandlerFunctionAdapter
createDefaultStrategy:用到createBean方法,这里参数 Class<?> clazz 是DispatcherServlet.properties文件中记录的
protected Object createDefaultStrategy(ApplicationContext context, Class<?> clazz) {
return context.getAutowireCapableBeanFactory().createBean(clazz);
}
创建完了HandlerMapping ,如何使用功能?
BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping:用 Aware接口 ApplicationContextAware 寻找Handler
public class BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping extends AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping {
}
BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping的寻找流程:
- 找出Spring容器中所有的beanName
- 判断beanName是不是以“/”开头
- 如果是,则把它当作一个Handler,并把beanName作为key,bean对象作为value存入handlerMap中
- handlerMap就是一个Map
BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping的一个父类ApplicationObjectsSupport:
实现 ApplicationContextAware
ApplicationContextAware接口的 setApplicationContext 方法
public interface ApplicationContextAware extends Aware {
void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException;
}
setApplicationContext最后会调用detectHandlers
protected void detectHandlers() throws BeansException {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = obtainApplicationContext();
String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlersInAncestorContexts ?
BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(applicationContext, Object.class) :
applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(Object.class));
// Take any bean name that we can determine URLs for.
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
String[] urls = determineUrlsForHandler(beanName);
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(urls)) {
// URL paths found: Let's consider it a handler.
registerHandler(urls, beanName);
}
}
if (mappingsLogger.isDebugEnabled()) {
mappingsLogger.debug(formatMappingName() + " " + getHandlerMap());
}
else if ((logger.isDebugEnabled() && !getHandlerMap().isEmpty()) || logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Detected " + getHandlerMap().size() + " mappings in " + formatMappingName());
}
}
determineUrlsForHandler方法:直接判断beanname是不是用/开头
protected String[] determineUrlsForHandler(String beanName) {
List<String> urls = new ArrayList<>();
if (beanName.startsWith("/")) {
urls.add(beanName);
}
String[] aliases = obtainApplicationContext().getAliases(beanName);
for (String alias : aliases) {
if (alias.startsWith("/")) {
urls.add(alias);
}
}
return StringUtils.toStringArray(urls);
}
registerHandler 注册到map中
protected void registerHandler(String[] urlPaths, String beanName) throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
Assert.notNull(urlPaths, "URL path array must not be null");
for (String urlPath : urlPaths) {
registerHandler(urlPath, beanName);
}
}
protected void registerHandler(String urlPath, Object handler) throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
Assert.notNull(urlPath, "URL path must not be null");
Assert.notNull(handler, "Handler object must not be null");
Object resolvedHandler = handler;
// Eagerly resolve handler if referencing singleton via name.
if (!this.lazyInitHandlers && handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
ApplicationContext applicationContext = obtainApplicationContext();
if (applicationContext.isSingleton(handlerName)) {
resolvedHandler = applicationContext.getBean(handlerName);
}
}
Object mappedHandler = this.handlerMap.get(urlPath);
if (mappedHandler != null) {
if (mappedHandler != resolvedHandler) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot map " + getHandlerDescription(handler) + " to URL path [" + urlPath +
"]: There is already " + getHandlerDescription(mappedHandler) + " mapped.");
}
}
else {
if (urlPath.equals("/")) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Root mapping to " + getHandlerDescription(handler));
}
setRootHandler(resolvedHandler);
}
else if (urlPath.equals("/*")) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Default mapping to " + getHandlerDescription(handler));
}
setDefaultHandler(resolvedHandler);
}
else {
this.handlerMap.put(urlPath, resolvedHandler);
if (getPatternParser() != null) {
this.pathPatternHandlerMap.put(getPatternParser().parse(urlPath), resolvedHandler);
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Mapped [" + urlPath + "] onto " + getHandlerDescription(handler));
}
}
}
}
存储在handlerMap
private final Map<String, Object> handlerMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
RequestMappingHandlerMapping:afterPropertiesSet来找有@RequestMapping的方法
RequestMappingHandlerMapping的寻找流程:
- 找出Spring容器中所有beanType
2 判断beanType是不是有@Controller注解,或者是不是有@RequestMapping注解 - 判断成功则继续找beanType中加了@RequestMapping的Method
- 并解析@RequestMapping中的内容,比如method、path,封装为一个RequestMappingInfo对象
- 最后把RequestMappingInfo对象做为key,Method对象封装为HandlerMethod对象后作为value,存入registry中
- registry就是一个Map
public class RequestMappingHandlerMapping extends RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping
implements MatchableHandlerMapping, EmbeddedValueResolverAware {
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
this.config = new RequestMappingInfo.BuilderConfiguration();
this.config.setTrailingSlashMatch(useTrailingSlashMatch()); // 尾部斜杠
this.config.setContentNegotiationManager(getContentNegotiationManager());
if (getPatternParser() != null) {
this.config.setPatternParser(getPatternParser());
Assert.isTrue(!this.useSuffixPatternMatch && !this.useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch,
"Suffix pattern matching not supported with PathPatternParser.");
}
else {
this.config.setSuffixPatternMatch(useSuffixPatternMatch());
this.config.setRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch(useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch());
this.config.setPathMatcher(getPathMatcher());
}
super.afterPropertiesSet();
}
}
父类afterPropertiesSet
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
initHandlerMethods();
}
initHandlerMethods方法:
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
// 获得所有候选beanName—— 当前容器所有的beanName
for (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) {
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
// *处理候选bean——即解析@RequestMapping和映射路径
processCandidateBean(beanName);
}
}
// 解析完所有@RequestMapping的时候调用
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
processCandidateBean方法:
protected void processCandidateBean(String beanName) {
Class<?> beanType = null;
try {
beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Could not resolve type for bean '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
// 这一步判断是关键 是否有Controller 或 RequestMapping注解
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
// 解析HandlerMethods
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
processCandidateBean方法中的obtainApplicationContext方法:获取spring容器
protected final ApplicationContext obtainApplicationContext() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = getApplicationContext();
Assert.state(applicationContext != null, "No ApplicationContext");
return applicationContext;
}
@Nullable
public final ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() throws IllegalStateException {
if (this.applicationContext == null && isContextRequired()) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"ApplicationObjectSupport instance [" + this + "] does not run in an ApplicationContext");
}
return this.applicationContext;
}
processCandidateBean方法中的isHandler:判断是不是有Controller注解或者RequestMapping注解
@Override
protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) {
return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) ||
AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class));
}
processCandidateBean方法中的detectHandlerMethods方法:解析
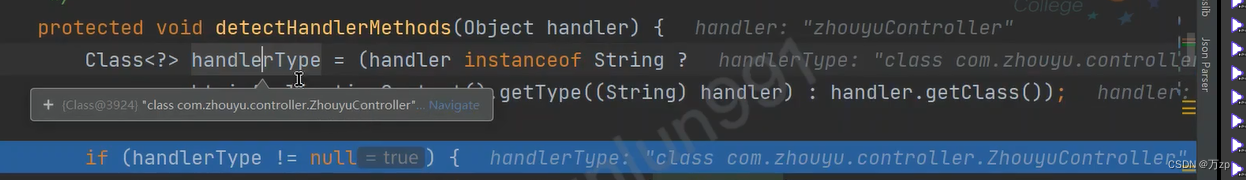
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) {
Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
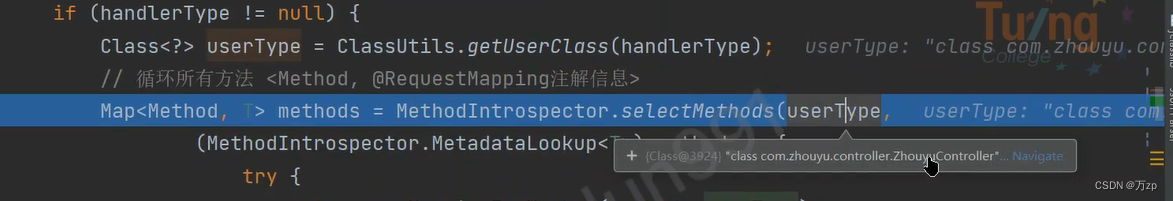
if (handlerType != null) {
Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
// 循环所有方法
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> {
try {
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +
userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);
}
});
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatMappings(userType, methods));
}
else if (mappingsLogger.isDebugEnabled()) {
mappingsLogger.debug(formatMappings(userType, methods));
}
methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> {
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType);
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
});
}
}
getMappingForMethod方法
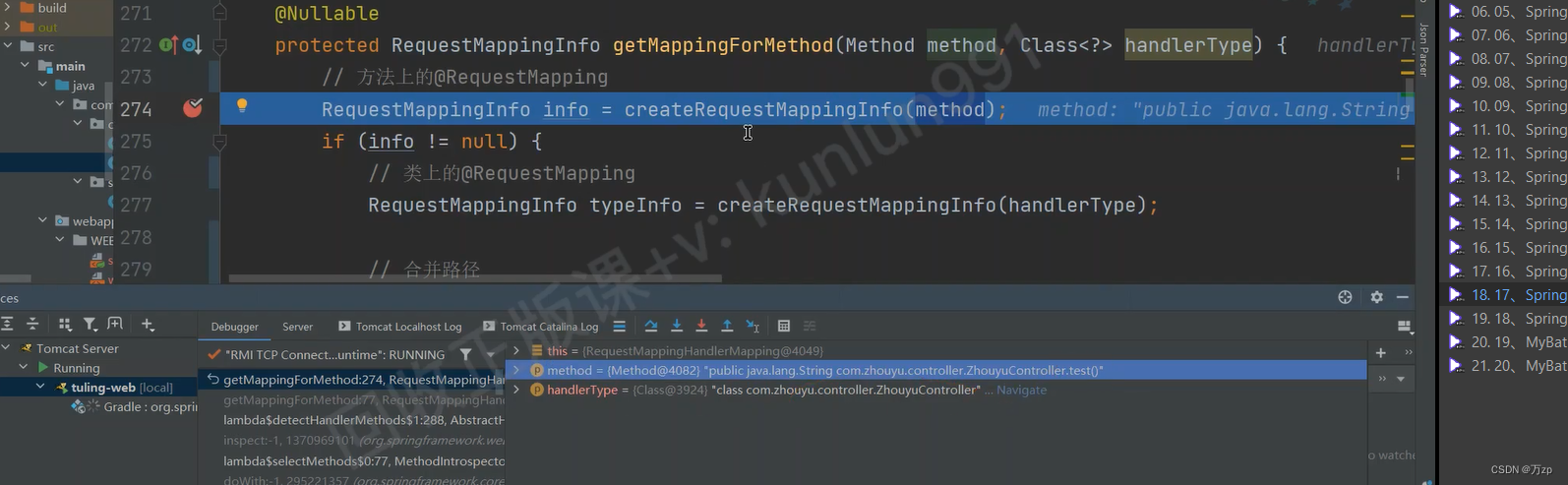
protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) {
// 如果方法上面有@RequestMapping:解析出RequestMappingInfo
// RequestMappingInfo 是用来在请求的时候做匹对的
RequestMappingInfo info = createRequestMappingInfo(method);
if (info != null) {
// 如果方法上面有@RequestMapping,看看类上面是不是有@RequestMapping
RequestMappingInfo typeInfo = createRequestMappingInfo(handlerType);
// 类上面也有@RequestMapping 那就合并
// 比如 类:/user 方法:/info 合并为 /user/info
if (typeInfo != null) {
info = typeInfo.combine(info);
}
// 合并前缀 5.1新增 默认null
// 可通过 WebMvcConfigurer#configurePathMatch 进行定制
String prefix = getPathPrefix(handlerType);
if (prefix != null) {
info = RequestMappingInfo.paths(prefix).options(this.config).build().combine(info);
}
}
return info;
}
createRequestMappingInfo:
@Nullable
private RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(AnnotatedElement element) {
// 获取RequestMapping注解
RequestMapping requestMapping = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(element, RequestMapping.class);
// 获取请求调解:[可扩展], 如果有:该条件会在请求时匹对
RequestCondition<?> condition = (element instanceof Class ?
getCustomTypeCondition((Class<?>) element) : getCustomMethodCondition((Method) element));
// 如果有RequestMapping注解,封装成RequestMappingInfo
return (requestMapping != null ? createRequestMappingInfo(requestMapping, condition) : null);
}
protected RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(
RequestMapping requestMapping, @Nullable RequestCondition<?> customCondition) {
// 将@RequestMapping注解属性的值构建成一个 RequestMappingInfo
RequestMappingInfo.Builder builder = RequestMappingInfo
//构建路径
.paths(resolveEmbeddedValuesInPatterns(requestMapping.path()))
//构建方法(get还是post等)
.methods(requestMapping.method())
//参数 对应http request parameter
.params(requestMapping.params())
//头部
.headers(requestMapping.headers())
//request的提交内容类型content type,如application/json, text/html
.consumes(requestMapping.consumes())
//指定返回的内容类型的content type,仅当request请求头中的(Accept)类型中包含该指定类型才返回
.produces(requestMapping.produces())
.mappingName(requestMapping.name());
if (customCondition != null) {
builder.customCondition(customCondition);
}
// 构造RequestMappingInfo:将上面的属性构建成一个个的RequestCondition对象方便在请求的时候组合匹对
return builder.options(this.config).build();
}
回到
detectHandlerMethods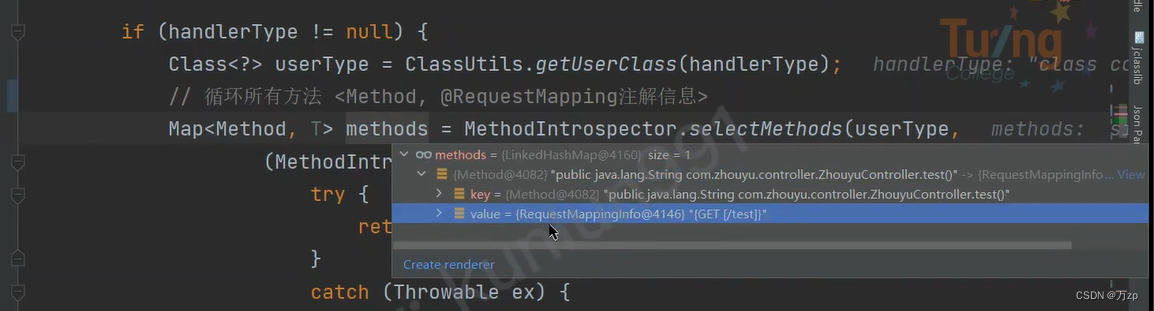
registerHandlerMethod
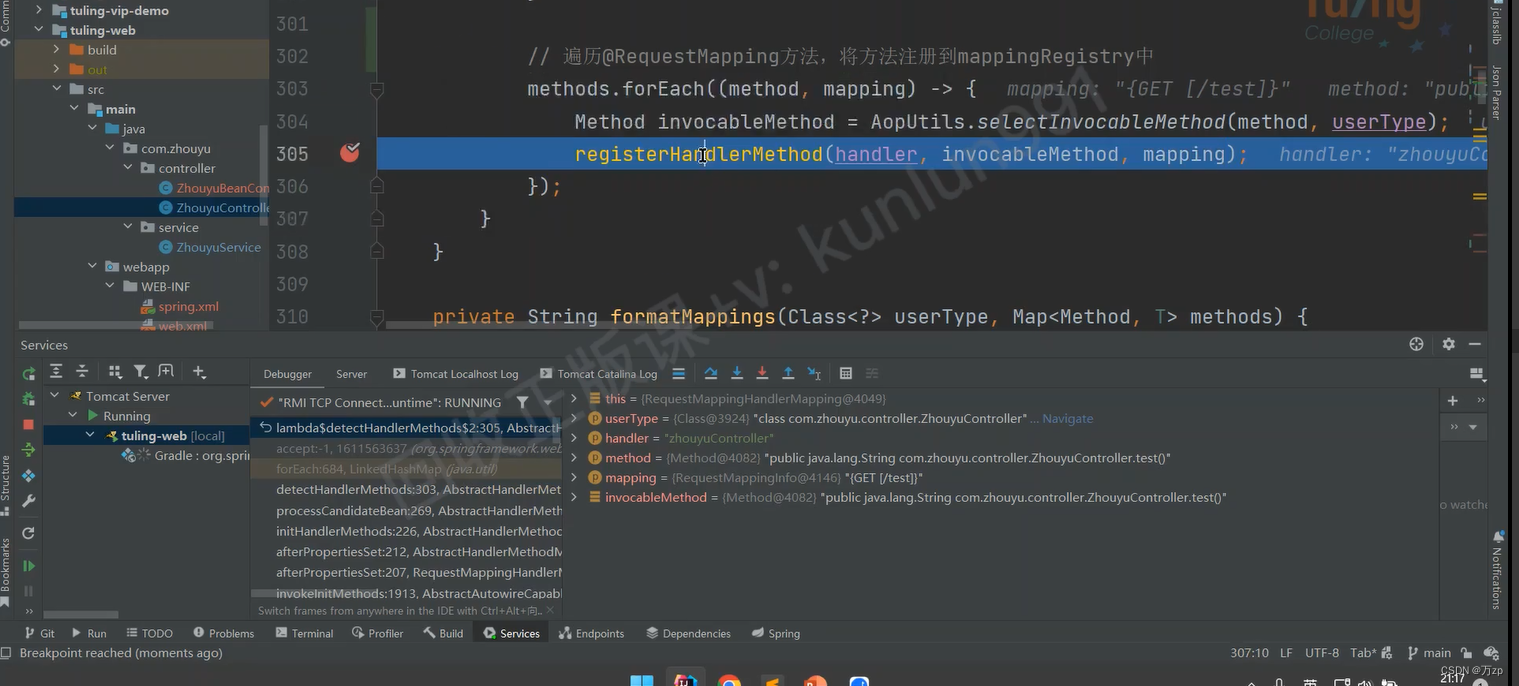
protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) {
this.mappingRegistry.register(mapping, handler, method);
}
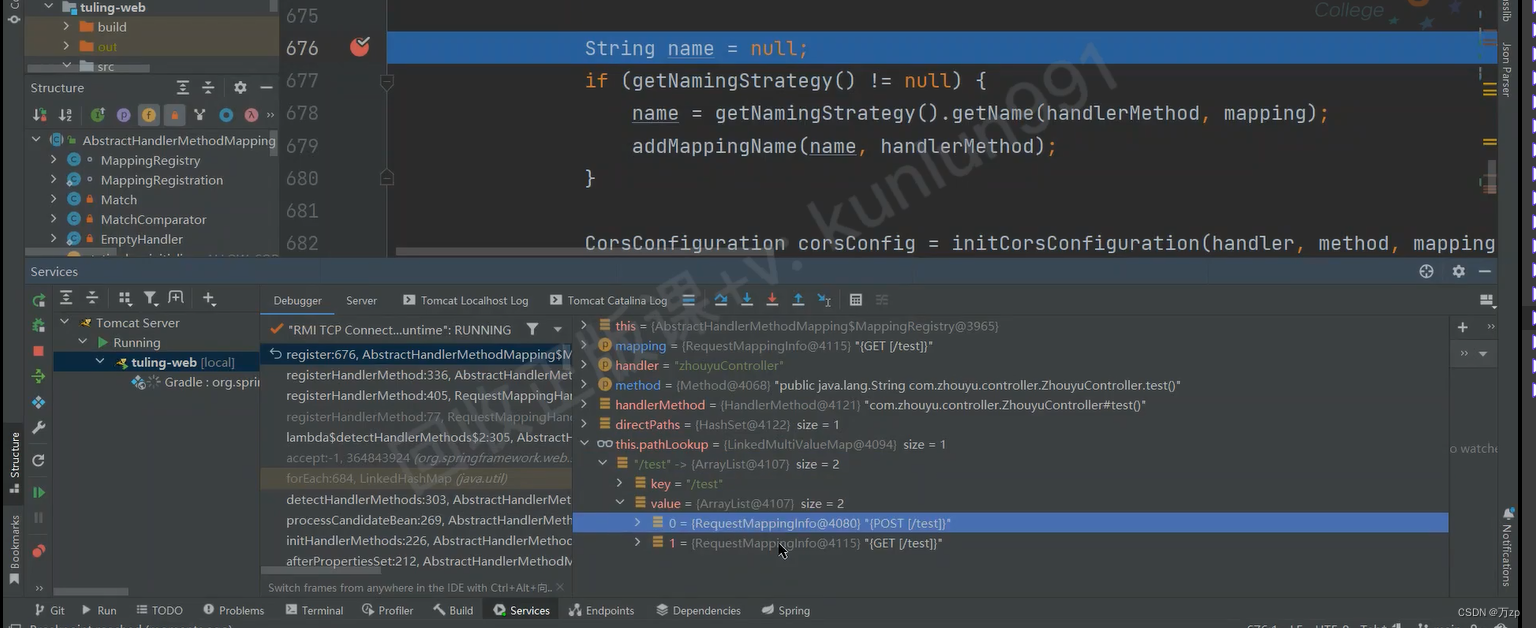
register
private final Map<T, MappingRegistration<T>> registry = new HashMap<>();
//辩别post,get方法,一个key,有多个值,值用链表
private final MultiValueMap<String, T> pathLookup = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
validateMethodMapping(handlerMethod, mapping);
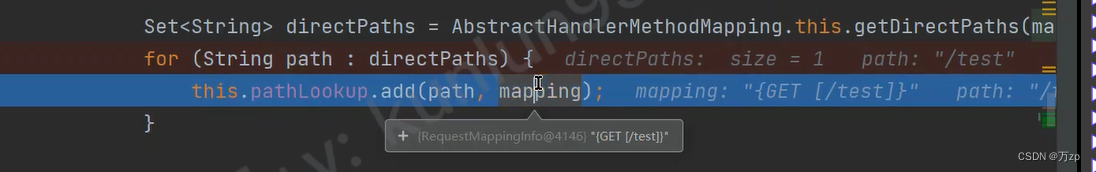
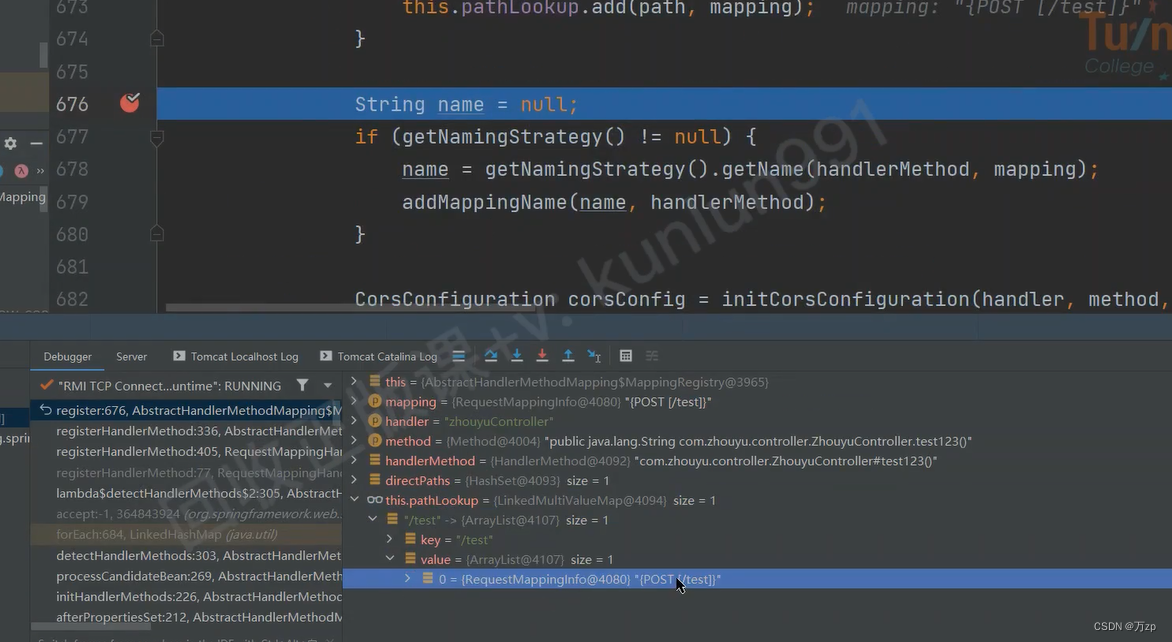
Set<String> directPaths = AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.this.getDirectPaths(mapping);
for (String path : directPaths) {
this.pathLookup.add(path, mapping);
}
String name = null;
if (getNamingStrategy() != null) {
name = getNamingStrategy().getName(handlerMethod, mapping);
addMappingName(name, handlerMethod);
}
CorsConfiguration corsConfig = initCorsConfiguration(handler, method, mapping);
if (corsConfig != null) {
corsConfig.validateAllowCredentials();
this.corsLookup.put(handlerMethod, corsConfig);
}
//
this.registry.put(mapping,
new MappingRegistration<>(mapping, handlerMethod, directPaths, name, corsConfig != null));
}
finally {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
RouterFunctionMapping:
RouterFunctionMapping的寻找流程会有些区别,但是大体是差不多的,相当于是一个path对应一个HandlerFunction。
public class RouterFunctionMapping extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
}

比较困难的点在于,当DispatcherServlet接收到一个请求时,该利用哪个HandlerMapping来寻找Handler呢?看源码:
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
很简单,就是遍历,找到就返回,默认顺序为:
所以BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping的优先级最高,比如:
@Component("/test")
public class ZhouyuBeanNameController implements Controller {
@Override
public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Hello zhouyu");
return new ModelAndView();
}
}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, path = "/test")
@ResponseBody
public String test(String username) {
return "Hi zhouyu";
}
14.什么是HandlerAdapter?
找到了Handler之后,接下来就该去执行了,比如执行下面这个test()
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, path = "/test")
@ResponseBody
public String test(String username) {
return "zhouyu";
}
但是由于有不同种类的Handler,所以执行方式是不一样的,再来总结一下Handler的类型:
- 实现了Controller接口的Bean对象,执行的是Bean对象中的handleRequest()
- 实现了HttpRequestHandler接口的Bean对象,执行的是Bean对象中的handleRequest()
- 添加了@RequestMapping注解的方法,具体为一个HandlerMethod,执行的就是当前加了注解的方法
- 一个HandlerFunction对象,执行的是HandlerFunction对象中的handle()
先初始化HandlerAdapter
initHandlerAdapters:
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
private void initHandlerAdapters(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerAdapters = null;
if (this.detectAllHandlerAdapters) {
// 查找容器中所有的 HandlerAdapter类型的Bean
Map<String, HandlerAdapter> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerAdapter.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerAdapters = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
// 排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerAdapters);
}
}
else {
try {
/* 只从容器中获取 BeanName = handlerAdapter HandlerAdapter类型的Bean */
HandlerAdapter ha = context.getBean("handlerAdapter", HandlerAdapter.class);
this.handlerAdapters = Collections.singletonList(ha);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
}
}
/**
* 没有自定义 使用默认的
*/
if (this.handlerAdapters == null) {
this.handlerAdapters = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerAdapter.class);
}
}
}
getDefaultStrategies:
protected <T> List<T> getDefaultStrategies(ApplicationContext context, Class<T> strategyInterface) {
String key = strategyInterface.getName();
/**
* 重点关注下这里 SpringMVC 的默认策略
*/
String value = defaultStrategies.getProperty(key);
if (value != null) {
/**
* 以 逗号 分割
*/
String[] classNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(value);
List<T> strategies = new ArrayList<>(classNames.length);
for (String className : classNames) {
try {
Class<?> clazz = ClassUtils.forName(className, DispatcherServlet.class.getClassLoader());
/**
* 这里是用 Web容器去创建实例
* 默认是多实例的(scope = provided)
*/
Object strategy = createDefaultStrategy(context, clazz);
strategies.add((T) strategy);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
}
catch (LinkageError err) {
}
}
return strategies;
}
else {
return new LinkedList<>();
}
}
createDefaultStrategy(context, clazz)
调用 Web容器的createBean创建Bean
HandlerAdapter一共四个
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.function.support.HandlerFunctionAdapter
15.springMVC响应http请求 给Handler一个HandlerAdapter
httpservlet service方法
protected abstract void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws Exception;
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
logRequest(request);
// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
if (this.flashMapManager != null) {
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
}
RequestPath previousRequestPath = null;
if (this.parseRequestPath) {
previousRequestPath = (RequestPath) request.getAttribute(ServletRequestPathUtils.PATH_ATTRIBUTE);
ServletRequestPathUtils.parseAndCache(request);
}
try {
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
if (this.parseRequestPath) {
ServletRequestPathUtils.setParsedRequestPath(previousRequestPath, request);
}
}
}
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// 进行映射
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// 找到最合适的HandlerAdapter
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler. HTTP缓存相关
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = HttpMethod.GET.matches(method);
if (isGet || HttpMethod.HEAD.matches(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
// 前置拦截器
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
// 返回false就不进行后续处理了
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
// 如果mv有 视图没有,给你设置默认视图
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
//后置拦截器
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
// 渲染视图
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
@Nullable
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
/** 拿到所有handlerMappings (容器启动阶段初始化:拿到所有实现了HandlerMapping的Bean)
* @see DispatcherServlet#initHandlerMappings
* 测试发现: 不同的HandlerMapping可以有相同path, 谁先解析到就用哪个
* */
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
if (this.handlerAdapters != null) {
for (HandlerAdapter adapter : this.handlerAdapters) {
if (adapter.supports(handler)) {
return adapter;
}
}
}
throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler +
"]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");
}
传入handler,遍历上面四个Adapter,谁支持就返回谁,比如判断的代码依次为:
HttpRequestHandlerAdapter :
HttpRequestHandlerAdapter, 该HttpRequestHandler接口的适配执行器
public class HttpRequestHandlerAdapter implements HandlerAdapter {
@Override
public boolean supports(Object handler) {
return (handler instanceof HttpRequestHandler);
}
}
SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter:
SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter, 该Controller接口的适配执行器
public class SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter implements HandlerAdapter {
@Override
public boolean supports(Object handler) {
return (handler instanceof Controller);
}
}
HandlerFunctionAdapter :
public class HandlerFunctionAdapter implements HandlerAdapter, Ordered {
@Override
public boolean supports(Object handler) {
return handler instanceof HandlerFunction;
}
}
@Nullable
ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception;
根据Handler适配出了对应的HandlerAdapter后,就执行具体HandlerAdapter对象的handle()方法了,比如:
public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
((HttpRequestHandler) handler).handleRequest(request, response);
return null;
}
public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
return ((Controller) handler).handleRequest(request, response);
}
HandlerFunction<?> handlerFunction = (HandlerFunction<?>) handler;
serverResponse = handlerFunction.handle(serverRequest);
智能推荐
JWT(Json Web Token)实现无状态登录_无状态token登录-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读685次。1.1.什么是有状态?有状态服务,即服务端需要记录每次会话的客户端信息,从而识别客户端身份,根据用户身份进行请求的处理,典型的设计如tomcat中的session。例如登录:用户登录后,我们把登录者的信息保存在服务端session中,并且给用户一个cookie值,记录对应的session。然后下次请求,用户携带cookie值来,我们就能识别到对应session,从而找到用户的信息。缺点是什么?服务端保存大量数据,增加服务端压力 服务端保存用户状态,无法进行水平扩展 客户端请求依赖服务.._无状态token登录
SDUT OJ逆置正整数-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读293次。SDUT OnlineJudge#include<iostream>using namespace std;int main(){int a,b,c,d;cin>>a;b=a%10;c=a/10%10;d=a/100%10;int key[3];key[0]=b;key[1]=c;key[2]=d;for(int i = 0;i<3;i++){ if(key[i]!=0) { cout<<key[i.
年终奖盲区_年终奖盲区表-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.2k次。年终奖采用的平均每月的收入来评定缴税级数的,速算扣除数也按照月份计算出来,但是最终减去的也是一个月的速算扣除数。为什么这么做呢,这样的收的税更多啊,年终也是一个月的收入,凭什么减去12*速算扣除数了?这个霸道(不要脸)的说法,我们只能合理避免的这些跨级的区域了,那具体是那些区域呢?可以参考下面的表格:年终奖一列标红的一对便是盲区的上下线,发放年终奖的数额一定一定要避免这个区域,不然公司多花了钱..._年终奖盲区表
matlab 提取struct结构体中某个字段所有变量的值_matlab读取struct类型数据中的值-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读7.5k次,点赞5次,收藏19次。matlab结构体struct字段变量值提取_matlab读取struct类型数据中的值
Android fragment的用法_android reader fragment-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读4.8k次。1,什么情况下使用fragment通常用来作为一个activity的用户界面的一部分例如, 一个新闻应用可以在屏幕左侧使用一个fragment来展示一个文章的列表,然后在屏幕右侧使用另一个fragment来展示一篇文章 – 2个fragment并排显示在相同的一个activity中,并且每一个fragment拥有它自己的一套生命周期回调方法,并且处理它们自己的用户输_android reader fragment
FFT of waveIn audio signals-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.8k次。FFT of waveIn audio signalsBy Aqiruse An article on using the Fast Fourier Transform on audio signals. IntroductionThe Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) allows users to view the spectrum content of _fft of wavein audio signals
随便推点
Awesome Mac:收集的非常全面好用的Mac应用程序、软件以及工具_awesomemac-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读5.9k次。https://jaywcjlove.github.io/awesome-mac/ 这个仓库主要是收集非常好用的Mac应用程序、软件以及工具,主要面向开发者和设计师。有这个想法是因为我最近发了一篇较为火爆的涨粉儿微信公众号文章《工具武装的前端开发工程师》,于是建了这么一个仓库,持续更新作为补充,搜集更多好用的软件工具。请Star、Pull Request或者使劲搓它 issu_awesomemac
java前端技术---jquery基础详解_简介java中jquery技术-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读616次。一.jquery简介 jQuery是一个快速的,简洁的javaScript库,使用户能更方便地处理HTML documents、events、实现动画效果,并且方便地为网站提供AJAX交互 jQuery 的功能概括1、html 的元素选取2、html的元素操作3、html dom遍历和修改4、js特效和动画效果5、css操作6、html事件操作7、ajax_简介java中jquery技术
Ant Design Table换滚动条的样式_ant design ::-webkit-scrollbar-corner-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.6w次,点赞5次,收藏19次。我修改的是表格的固定列滚动而产生的滚动条引用Table的组件的css文件中加入下面的样式:.ant-table-body{ &amp;::-webkit-scrollbar { height: 5px; } &amp;::-webkit-scrollbar-thumb { border-radius: 5px; -webkit-box..._ant design ::-webkit-scrollbar-corner
javaWeb毕设分享 健身俱乐部会员管理系统【源码+论文】-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读269次。基于JSP的健身俱乐部会员管理系统项目分享:见文末!
论文开题报告怎么写?_开题报告研究难点-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.8k次,点赞2次,收藏15次。同学们,是不是又到了一年一度写开题报告的时候呀?是不是还在为不知道论文的开题报告怎么写而苦恼?Take it easy!我带着倾尽我所有开题报告写作经验总结出来的最强保姆级开题报告解说来啦,一定让你脱胎换骨,顺利拿下开题报告这个高塔,你确定还不赶快点赞收藏学起来吗?_开题报告研究难点
原生JS 与 VUE获取父级、子级、兄弟节点的方法 及一些DOM对象的获取_获取子节点的路径 vue-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读6k次,点赞4次,收藏17次。原生先获取对象var a = document.getElementById("dom");vue先添加ref <div class="" ref="divBox">获取对象let a = this.$refs.divBox获取父、子、兄弟节点方法var b = a.childNodes; 获取a的全部子节点 var c = a.parentNode; 获取a的父节点var d = a.nextSbiling; 获取a的下一个兄弟节点 var e = a.previ_获取子节点的路径 vue