【Springboot】笔记1-程序员宅基地
技术标签: spring boot 笔记 Javaee 后端
在B站边看视频边补充笔记,是在b站那里获取的文档和资料,自己进行笔记的修修改改,仅供参考,方便个人使用的,在源码分析部分,我感觉我看的不是很懂,有没有大佬分享一下源码分析的方法或者技巧,我一看源码就犯困!!!
文章目录
-
- 01、基础入门-SpringBoot2课程介绍
- 02、基础入门-Spring生态圈
- 03、基础入门-SpringBoot的大时代背景
- 04、基础入门-SpringBoot官方文档架构
- 05、基础入门-SpringBoot-HelloWorld
- 06、基础入门-SpringBoot-依赖管理特性
- 07、基础入门-SpringBoot-自动配置特性
- 08、底层注解-@Configuration详解
- 09、底层注解-@Import导入组件
- 10、底层注解-@Conditional条件装配
- 11、底层注解-@ImportResource导入Spring配置文件
- 12、底层注解-@ConfigurationProperties配置绑定
- 13、自动配置【源码分析】-自动包规则原理
- 14、自动配置【源码分析】-初始加载自动配置类
- 15、自动配置【源码分析】-自动配置流程
- 16、最佳实践-SpringBoot应用如何编写
- 17、最佳实践-Lombok简化开发
- 18、最佳实践-dev-tools
- 19、最佳实践-Spring Initailizr
- 20、配置文件-yaml的用法
- 21、配置文件-自定义类绑定的配置提示
- 22、web场景-web开发简介
- 23、web场景-静态资源规则与定制化
- 24、web场景-welcome与favicon功能
- 25、web场景-【源码分析】-静态资源原理
- 26、请求处理-【源码分析】-Rest映射及源码解析
- 27、请求处理-【源码分析】-怎么改变默认的\_method
- 28、请求处理-【源码分析】-请求映射原理
- 29、请求处理-常用参数注解使用
- 30、请求处理-@RequestAttribute
- 31、请求处理-@MatrixVariable与UrlPathHelper
- 32、请求处理-【源码分析】-各种类型参数解析原理
- 33、请求处理-【源码分析】-Servlet API参数解析原理
- 34、请求处理-【源码分析】-Model、Map原理
- 35、请求处理-【源码分析】-自定义参数绑定原理
- 36、请求处理-【源码分析】-自定义Converter原理
- 37、响应处理-【源码分析】-ReturnValueHandler原理
- 38、响应处理-【源码分析】-HTTPMessageConverter原理
- 39、响应处理-【源码分析】-内容协商原理
- 40、响应处理-【源码分析】-基于请求参数的内容协商原理
- 41、响应处理-【源码分析】-自定义MessageConverter
- 42、响应处理-【源码分析】-浏览器与PostMan内容协商完全适配
- 43、视图解析-Thymeleaf初体验
- 44、web实验-后台管理系统基本功能
01、基础入门-SpringBoot2课程介绍
-
Spring Boot 2核心技术
-
Spring Boot 2响应式编程
- 学习要求
-熟悉Spring基础
-熟悉Maven使用 - 环境要求
- Java8及以上
- Maven 3.3及以上
- 学习资料
02、基础入门-Spring生态圈
Spring能做什么
Spring的能力

Spring的生态
覆盖了:
- web开发
- 数据访问
- 安全控制
- 分布式
- 消息服务
- 移动开发
- 批处理
- …
Spring5重大升级
- 响应式编程

- 内部源码设计
基于Java8的一些新特性,如:接口默认实现。重新设计源码架构。
为什么用SpringBoot
Spring Boot makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring based Applications that you can “just run”.link
能快速创建出生产级别的Spring应用。
SpringBoot优点
-
Create stand-alone Spring applications
- 创建独立Spring应用
-
Embed Tomcat, Jetty or Undertow directly (no need to deploy WAR files)
- 内嵌web服务器
-
Provide opinionated ‘starter’ dependencies to simplify your build configuration
- 自动starter依赖,简化构建配置
-
Automatically configure Spring and 3rd party libraries whenever possible
- 自动配置Spring以及第三方功能
-
Provide production-ready features such as metrics, health checks, and externalized configuration
- 提供生产级别的监控、健康检查及外部化配置
-
Absolutely no code generation and no requirement for XML configuration
- 无代码生成、无需编写XML
-
SpringBoot是整合Spring技术栈的一站式框架
-
SpringBoot是简化Spring技术栈的快速开发脚手架
SpringBoot缺点
- 人称版本帝,迭代快,需要时刻关注变化
- 封装太深,内部原理复杂,不容易精通
03、基础入门-SpringBoot的大时代背景
微服务
In short, the microservice architectural style is an approach to developing a single application as a suite of small services, each running in its own process and communicating with lightweight mechanisms, often an HTTP resource API. These services are built around business capabilities and independently deployable by fully automated deployment machinery. There is a bare minimum of centralized management of these services, which may be written in different programming languages and use different data storage technologies.——James Lewis and Martin Fowler (2014)
- 微服务是一种架构风格
- 一个应用拆分为一组小型服务
- 每个服务运行在自己的进程内,也就是可独立部署和升级
- 服务之间使用轻量级HTTP交互
- 服务围绕业务功能拆分
- 可以由全自动部署机制独立部署
- 去中心化,服务自治。服务可以使用不同的语言、不同的存储技术
分布式

分布式的困难
- 远程调用
- 服务发现
- 负载均衡
- 服务容错
- 配置管理
- 服务监控
- 链路追踪
- 日志管理
- 任务调度
- …
分布式的解决
- SpringBoot + SpringCloud

云原生
原生应用如何上云。 Cloud Native
上云的困难
- 服务自愈
- 弹性伸缩
- 服务隔离
- 自动化部署
- 灰度发布
- 流量治理
- …
上云的解决

04、基础入门-SpringBoot官方文档架构
官网文档架构



05、基础入门-SpringBoot-HelloWorld
系统要求
- Java 8
- Maven 3.3+
- IntelliJ IDEA 2019.1.2
Maven配置文件
新添内容:
<mirrors>
<mirror>
<id>nexus-aliyun</id>
<mirrorOf>central</mirrorOf>
<name>Nexus aliyun</name>
<url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public</url>
</mirror>
</mirrors>
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>jdk-1.8</id>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
<jdk>1.8</jdk>
</activation>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<maven.compiler.compilerVersion>1.8</maven.compiler.compilerVersion>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>
HelloWorld项目
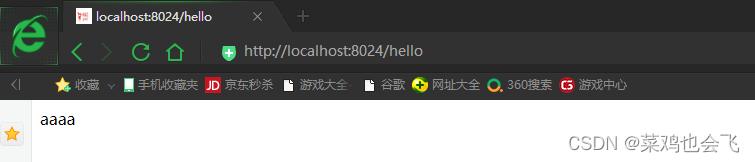
需求:浏览发送/hello请求,响应 “Hello,Spring Boot 2”
创建maven工程
引入依赖
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
创建主程序
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class MainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class, args);
}
}
编写业务
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String handle01(){
return "Hello, Spring Boot 2!";
}
}
运行&测试
- 运行
MainApplication类 - 浏览器输入
http://localhost:8888/hello,将会输出Hello, Spring Boot 2!。
设置配置
maven工程的resource文件夹中创建application.properties文件。
# 设置端口号
server.port=8888
打包部署
在pom.xml添加
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
在IDEA的Maven插件上点击运行 clean 、package,把helloworld工程项目的打包成jar包,
打包好的jar包被生成在helloworld工程项目的target文件夹内。
用cmd运行java -jar boot-01-helloworld-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar,既可以运行helloworld工程项目。
将jar包直接在目标服务器执行即可。
06、基础入门-SpringBoot-依赖管理特性
- 父项目做依赖管理
依赖管理
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
上面项目的父项目如下:
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
它几乎声明了所有开发中常用的依赖的版本号,自动版本仲裁机制
- 开发导入starter场景启动器
- 见到很多 spring-boot-starter-* : *就某种场景
- 只要引入starter,这个场景的所有常规需要的依赖我们都自动引入
- 更多SpringBoot所有支持的场景
- 见到的 *-spring-boot-starter: 第三方为我们提供的简化开发的场景启动器。
所有场景启动器最底层的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
-
无需关注版本号,自动版本仲裁
- 引入依赖默认都可以不写版本
- 引入非版本仲裁的jar,要写版本号。
-
可以修改默认版本号
- 查看spring-boot-dependencies里面规定当前依赖的版本 用的 key。
- 在当前项目里面重写配置,如下面的代码。
<properties>
<mysql.version>5.1.43</mysql.version>
</properties>
IDEA快捷键:
-
ctrl + shift + alt + U:以图的方式显示项目中依赖之间的关系。
-
alt + ins:相当于Eclipse的 Ctrl + N,创建新类,新包等。
07、基础入门-SpringBoot-自动配置特性
- 自动配好Tomcat
- 引入Tomcat依赖。
- 配置Tomcat
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
-
自动配好SpringMVC
- 引入SpringMVC全套组件
- 自动配好SpringMVC常用组件(功能)
-
自动配好Web常见功能,如:字符编码问题
- SpringBoot帮我们配置好了所有web开发的常见场景
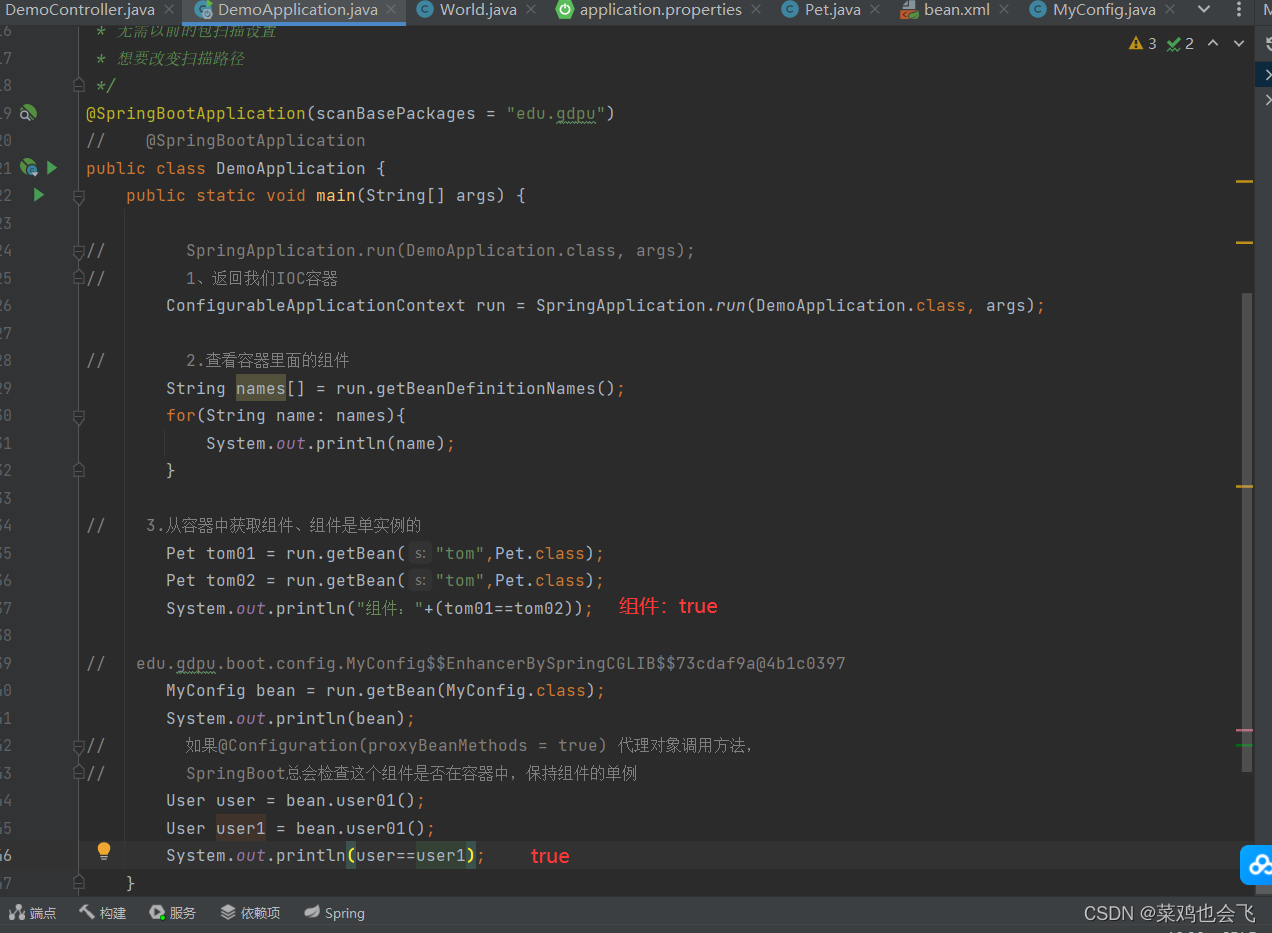
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、返回我们IOC容器
ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class, args);
//2、查看容器里面的组件
String[] names = run.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
- 默认的包结构
- 主程序所在包及其下面的所有子包里面的组件都会被默认扫描进来
- 无需以前的包扫描配置
- 想要改变扫描路径
- @SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages=“edu.gdpu”)
- @ComponentScan 指定扫描路径
@SpringBootApplication
等同于
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan("edu.gdpu")
-
各种配置拥有默认值
- 默认配置最终都是映射到某个类上,如:
MultipartProperties - 配置文件的值最终会绑定每个类上,这个类会在容器中创建对象
- 默认配置最终都是映射到某个类上,如:
-
按需加载所有自动配置项
- 非常多的starter
- 引入了哪些场景这个场景的自动配置才会开启
- SpringBoot所有的自动配置功能都在 spring-boot-autoconfigure 包里面
-
…
08、底层注解-@Configuration详解
项目结构:
- 基本使用
- Full模式与Lite模式
- 示例
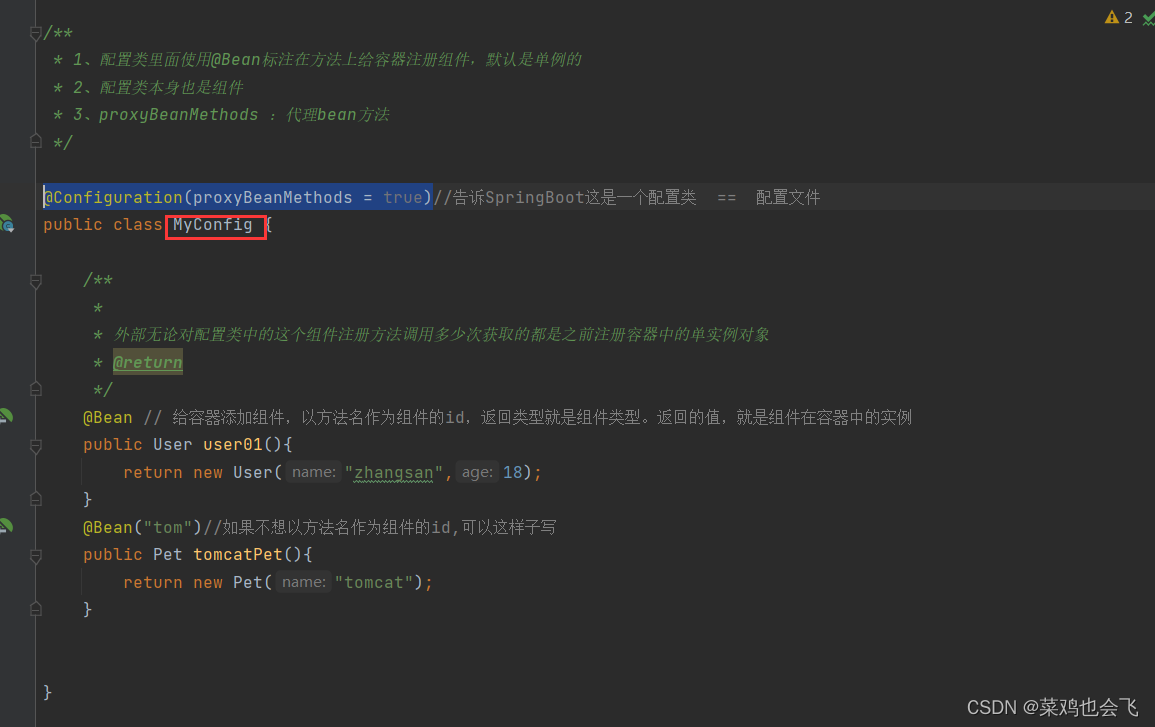
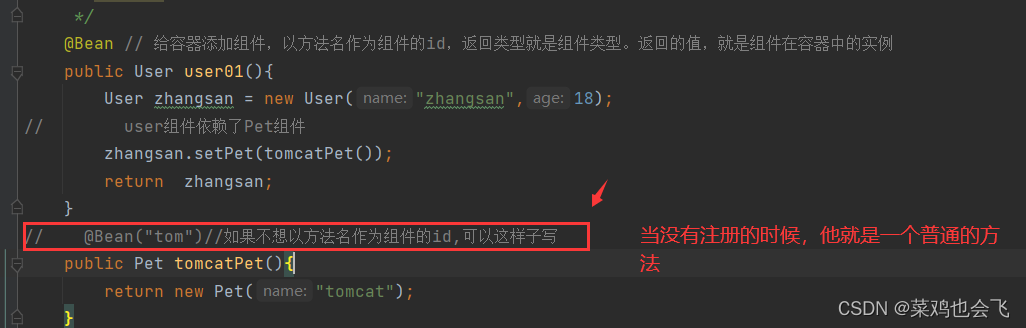
/**
* 1、配置类里面使用@Bean标注在方法上给容器注册组件,默认也是单实例的
* 2、配置类本身也是组件
* 3、proxyBeanMethods:代理bean的方法
* Full(proxyBeanMethods = true)(保证每个@Bean方法被调用多少次返回的组件都是单实例的)(默认)
* Lite(proxyBeanMethods = false)(每个@Bean方法被调用多少次返回的组件都是新创建的)
*/
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) //告诉SpringBoot这是一个配置类 == 配置文件
public class MyConfig {
/**
* Full:外部无论对配置类中的这个组件注册方法调用多少次获取的都是之前注册容器中的单实例对象
* @return
*/
@Bean //给容器中添加组件。以方法名作为组件的id。返回类型就是组件类型。返回的值,就是组件在容器中的实例
public User user01(){
User zhangsan = new User("zhangsan", 18);
//user组件依赖了Pet组件
zhangsan.setPet(tomcatPet());
return zhangsan;
}
@Bean("tom")
public Pet tomcatPet(){
return new Pet("tomcat");
}
}
@Configuration测试代码如下:
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan("com.atguigu.boot")
public class MainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、返回我们IOC容器
ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class, args);
//2、查看容器里面的组件
String[] names = run.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
//3、从容器中获取组件
Pet tom01 = run.getBean("tom", Pet.class);
Pet tom02 = run.getBean("tom", Pet.class);
System.out.println("组件:"+(tom01 == tom02));
//4、com.atguigu.boot.config.MyConfig$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$51f1e1ca@1654a892
MyConfig bean = run.getBean(MyConfig.class);
System.out.println(bean);
//如果@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = true)代理对象调用方法。SpringBoot总会检查这个组件是否在容器中有。
//保持组件单实例
User user = bean.user01();
User user1 = bean.user01();
System.out.println(user == user1);
User user01 = run.getBean("user01", User.class);
Pet tom = run.getBean("tom", Pet.class);
System.out.println("用户的宠物:"+(user01.getPet() == tom));
}
}
- 最佳实战
- 配置 类组件之间无依赖关系用Lite模式加速容器启动过程,减少判断
- 配置 类组件之间有依赖关系,方法会被调用得到之前单实例组件,用Full模式(默认)
lite 英 [laɪt] 美 [laɪt]
adj. 低热量的,清淡的(light的一种拼写方法);类似…的劣质品
IDEA快捷键:
Alt + Ins:生成getter,setter、构造器等代码。Ctrl + Alt + B:查看类的具体实现代码。
09、底层注解-@Import导入组件
@Bean、@Component、@Controller、@Service、@Repository,它们是Spring的基本标签,在Spring Boot中并未改变它们原来的功能。
@ComponentScan 在07、基础入门-SpringBoot-自动配置特性有用例。
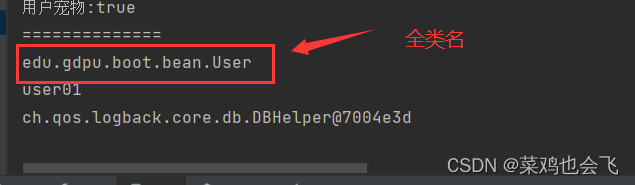
@Import({User.class, DBHelper.class})给容器中自动创建出这两个类型的组件、默认组件的名字就是全类名
@Import({
User.class, DBHelper.class})
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) //告诉SpringBoot这是一个配置类 == 配置文件
public class MyConfig {
}
测试类:
//1、返回我们IOC容器
ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class, args);
//...
//5、获取组件
String[] beanNamesForType = run.getBeanNamesForType(User.class);
for (String s : beanNamesForType) {
System.out.println(s);
}
DBHelper bean1 = run.getBean(DBHelper.class);
System.out.println(bean1);
10、底层注解-@Conditional条件装配
条件装配:满足Conditional指定的条件,则进行组件注入

用@ConditionalOnBean举例说明
用@ConditionalOnMissingBean举例说明
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
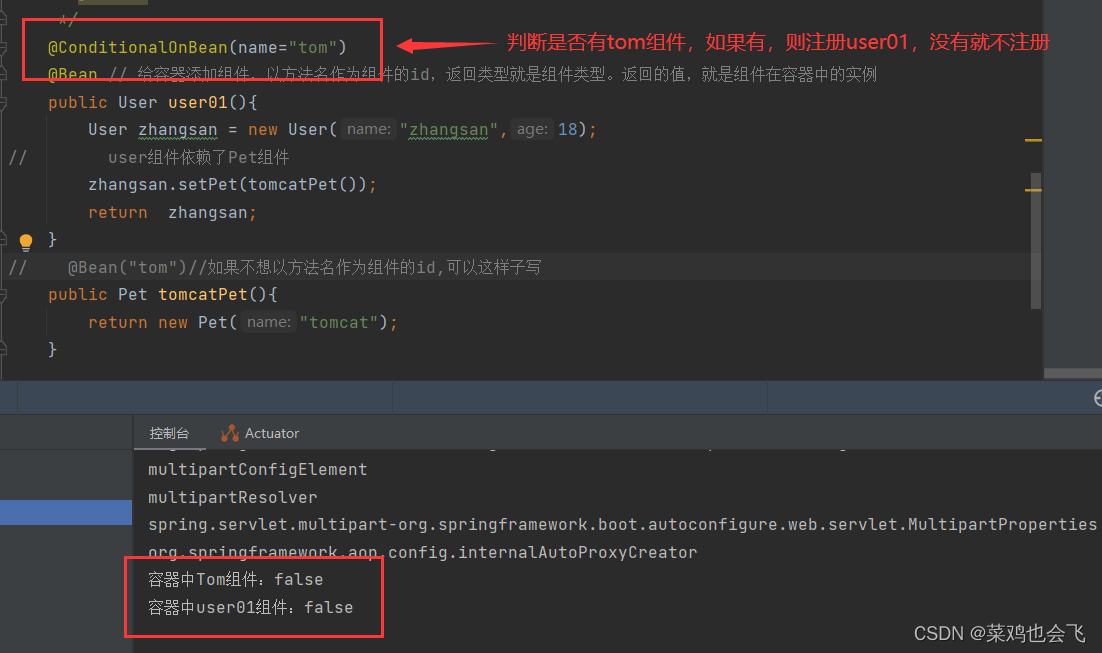
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "tom")//没有tom名字的Bean时,MyConfig类的Bean才能生效。
public class MyConfig {
@Bean
public User user01(){
User zhangsan = new User("zhangsan", 18);
zhangsan.setPet(tomcatPet());
return zhangsan;
}
@Bean("tom22")
public Pet tomcatPet(){
return new Pet("tomcat");
}
}
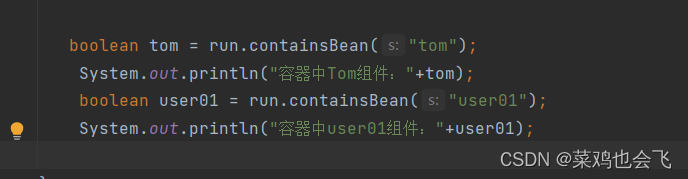
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、返回我们IOC容器
ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class, args);
//2、查看容器里面的组件
String[] names = run.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
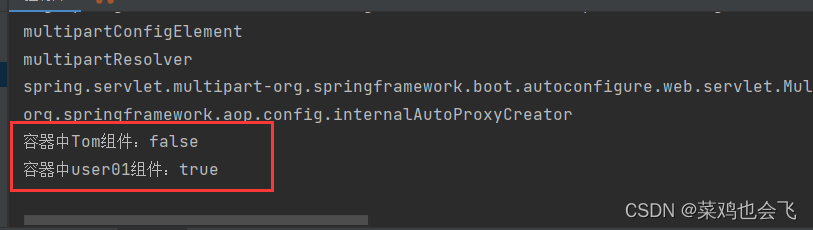
boolean tom = run.containsBean("tom");
System.out.println("容器中Tom组件:"+tom);//false
boolean user01 = run.containsBean("user01");
System.out.println("容器中user01组件:"+user01);//true
boolean tom22 = run.containsBean("tom22");
System.out.println("容器中tom22组件:"+tom22);//true
}
11、底层注解-@ImportResource导入Spring配置文件
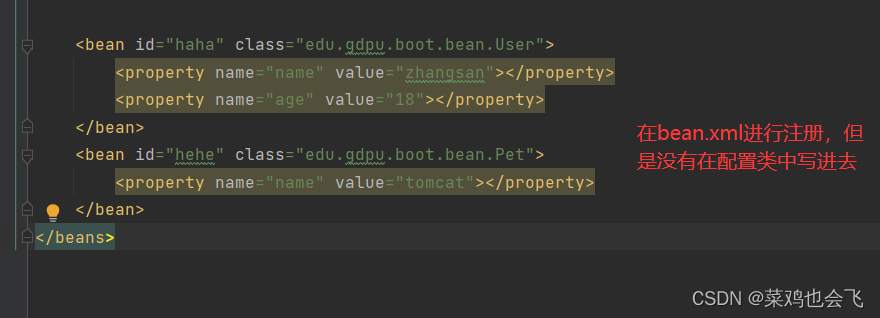
比如,公司使用bean.xml文件生成配置bean,然而你为了省事,想继续复用bean.xml,@ImportResource粉墨登场。
bean.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans ...">
<bean id="haha" class="com.lun.boot.bean.User">
<property name="name" value="zhangsan"></property>
<property name="age" value="18"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="hehe" class="com.lun.boot.bean.Pet">
<property name="name" value="tomcat"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
使用方法:
@ImportResource("classpath:beans.xml")
public class MyConfig {
...
}
测试类:
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、返回我们IOC容器
ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class, args);
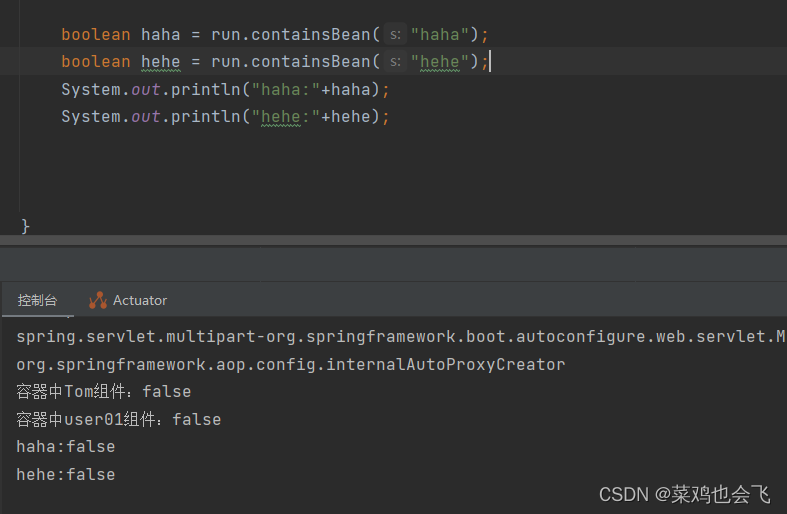
boolean haha = run.containsBean("haha");
boolean hehe = run.containsBean("hehe");
System.out.println("haha:"+haha);//true
System.out.println("hehe:"+hehe);//true
}

12、底层注解-@ConfigurationProperties配置绑定
复习相关知识点

如何使用Java读取到properties文件中的内容,并且把它封装到JavaBean中,以供随时使用
传统方法:
public class getProperties {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
Properties pps = new Properties();
pps.load(new FileInputStream("a.properties"));
Enumeration enum1 = pps.propertyNames();//得到配置文件的名字
while(enum1.hasMoreElements()) {
String strKey = (String) enum1.nextElement();
String strValue = pps.getProperty(strKey);
System.out.println(strKey + "=" + strValue);
//封装到JavaBean。
}
}
}
Spring Boot一种配置配置绑定:
@ConfigurationProperties + @Component
假设有配置文件application.properties
mycar.brand=BYD
mycar.price=100000
只有在容器中的组件,才会拥有SpringBoot提供的强大功能
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mycar")
public class Car {
...
}
Spring Boot另一种配置配置绑定:
@EnableConfigurationProperties + @ConfigurationProperties
- 开启Car配置绑定功能
- 把这个Car这个组件自动注册到容器中
@EnableConfigurationProperties(Car.class)
public class MyConfig {
...
}
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mycar")
public class Car {
...
}
13、自动配置【源码分析】-自动包规则原理
Spring Boot应用的启动类:
@SpringBootApplication
public class MainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class, args);
}
}
分析下@SpringBootApplication
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(
excludeFilters = {
@Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {
TypeExcludeFilter.class}
), @Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {
AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class}
)}
)
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
...
}
重点分析@SpringBootConfiguration,@EnableAutoConfiguration,@ComponentScan。
@SpringBootConfiguration
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Configuration
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {
@AliasFor(
annotation = Configuration.class
)
boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true;
}
@Configuration代表当前是一个配置类。
@ComponentScan
指定扫描哪些Spring注解。
@ComponentScan 在07、基础入门-SpringBoot-自动配置特性有用例。
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration";
Class<?>[] exclude() default {
};
String[] excludeName() default {
};
}
重点分析@AutoConfigurationPackage,@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)。
@AutoConfigurationPackage
标签名直译为:自动配置包,指定了默认的包规则。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)//给容器中导入一个组件
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {
String[] basePackages() default {
};
Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {
};
}
- 利用Registrar给容器中导入一系列组件
- 将指定的一个包下的所有组件导入进MainApplication所在包下。
14、自动配置【源码分析】-初始加载自动配置类
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
- 利用
getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata);给容器中批量导入一些组件 - 调用
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes)获取到所有需要导入到容器中的配置类 - 利用工厂加载
Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader);得到所有的组件 - 从
META-INF/spring.factories位置来加载一个文件。- 默认扫描我们当前系统里面所有
META-INF/spring.factories位置的文件 spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.3.4.RELEASE.jar包里面也有META-INF/spring.factories
- 默认扫描我们当前系统里面所有
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-faMdLhME-1689300375201)(image/20210205005536620.png)]
# 文件里面写死了spring-boot一启动就要给容器中加载的所有配置类
# spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.3.4.RELEASE.jar/META-INF/spring.factories
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\
...
虽然我们127个场景的所有自动配置启动的时候默认全部加载,但是xxxxAutoConfiguration按照条件装配规则(@Conditional),最终会按需配置。
如AopAutoConfiguration类:
@Configuration(
proxyBeanMethods = false
)
@ConditionalOnProperty(
prefix = "spring.aop",
name = "auto",
havingValue = "true",
matchIfMissing = true
)
public class AopAutoConfiguration {
public AopAutoConfiguration() {
}
...
}
15、自动配置【源码分析】-自动配置流程
以DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration的内部类DispatcherServletConfiguration为例子:
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(MultipartResolver.class) //容器中有这个类型组件
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = DispatcherServlet.MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME) //容器中没有这个名字 multipartResolver 的组件
public MultipartResolver multipartResolver(MultipartResolver resolver) {
//给@Bean标注的方法传入了对象参数,这个参数的值就会从容器中找。
//SpringMVC multipartResolver。防止有些用户配置的文件上传解析器不符合规范
// Detect if the user has created a MultipartResolver but named it incorrectly
return resolver;//给容器中加入了文件上传解析器;
}
SpringBoot默认会在底层配好所有的组件,但是如果用户自己配置了以用户的优先。
总结:
- SpringBoot先加载所有的自动配置类 xxxxxAutoConfiguration
- 每个自动配置类按照条件进行生效,默认都会绑定配置文件指定的值。(xxxxProperties里面读取,xxxProperties和配置文件进行了绑定)
- 生效的配置类就会给容器中装配很多组件
- 只要容器中有这些组件,相当于这些功能就有了
- 定制化配置
- 用户直接自己@Bean替换底层的组件
- 用户去看这个组件是获取的配置文件什么值就去修改。
xxxxxAutoConfiguration —> 组件 —> xxxxProperties里面拿值 ----> application.properties
16、最佳实践-SpringBoot应用如何编写
- 引入场景依赖
- 查看自动配置了哪些(选做)
- 自己分析,引入场景对应的自动配置一般都生效了
- 配置文件中debug=true开启自动配置报告。
- Negative(不生效)
- Positive(生效)
- 是否需要修改
- 参照文档修改配置项
- 官方文档
- 自己分析。xxxxProperties绑定了配置文件的哪些。
- 自定义加入或者替换组件
- @Bean、@Component…
- 自定义器 XXXXXCustomizer;
- …
- 参照文档修改配置项
17、最佳实践-Lombok简化开发
Lombok用标签方式代替构造器、getter/setter、toString()等鸡肋代码。
spring boot已经管理Lombok。引入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
IDEA中File->Settings->Plugins,搜索安装Lombok插件。
@NoArgsConstructor
//@AllArgsConstructor
@Data
@ToString
@EqualsAndHashCode
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Pet pet;
public User(String name,Integer age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
简化日志开发
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String handle01(@RequestParam("name") String name){
log.info("请求进来了....");
return "Hello, Spring Boot 2!"+"你好:"+name;
}
}
18、最佳实践-dev-tools
Spring Boot includes an additional set of tools that can make the application development experience a little more pleasant. The
spring-boot-devtoolsmodule can be included in any project to provide additional development-time features.——linkApplications that use
spring-boot-devtoolsautomatically restart whenever files on the classpath change. This can be a useful feature when working in an IDE, as it gives a very fast feedback loop for code changes. By default, any entry on the classpath that points to a directory is monitored for changes. Note that certain resources, such as static assets and view templates, do not need to restart the application.——linkTriggering a restart
As DevTools monitors classpath resources, the only way to trigger a restart is to update the classpath. The way in which you cause the classpath to be updated depends on the IDE that you are using:
- In Eclipse, saving a modified file causes the classpath to be updated and triggers a restart.
- In IntelliJ IDEA, building the project (
Build -> Build Project)(shortcut: Ctrl+F9) has the same effect.
添加依赖:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
在IDEA中,项目或者页面修改以后:Ctrl+F9。
19、最佳实践-Spring Initailizr
Spring Initailizr是创建Spring Boot工程向导。
在IDEA中,菜单栏New -> Project -> Spring Initailizr。
20、配置文件-yaml的用法
同以前的properties用法
YAML 是 “YAML Ain’t Markup Language”(YAML 不是一种标记语言)的递归缩写。在开发的这种语言时,YAML 的意思其实是:“Yet Another Markup Language”(仍是一种标记语言)。
非常适合用来做以数据为中心的配置文件。
基本语法
- key: value;kv之间有空格
- 大小写敏感
- 使用缩进表示层级关系
- 缩进不允许使用tab,只允许空格
- 缩进的空格数不重要,只要相同层级的元素左对齐即可
- '#'表示注释
- 字符串无需加引号,如果要加,单引号’'、双引号""表示字符串内容会被 转义、不转义
数据类型
- 字面量:单个的、不可再分的值。date、boolean、string、number、null
k: v
- 对象:键值对的集合。map、hash、set、object
#行内写法:
k: {
k1:v1,k2:v2,k3:v3}
#或
k:
k1: v1
k2: v2
k3: v3
- 数组:一组按次序排列的值。array、list、queue
#行内写法:
k: [v1,v2,v3]
#或者
k:
- v1
- v2
- v3
实例
@Data
public class Person {
private String userName;
private Boolean boss;
private Date birth;
private Integer age;
private Pet pet;
private String[] interests;
private List<String> animal;
private Map<String, Object> score;
private Set<Double> salarys;
private Map<String, List<Pet>> allPets;
}
@Data
public class Pet {
private String name;
private Double weight;
}
用yaml表示以上对象
person:
username: zhangsan
boss: true
birth: 2023/7/15
age: 18
# interests: [篮球,足球]
interests:
- 篮球
- 足球
- 羽毛球
animal: [阿猫,阿狗]
# score:
# english: 78
# math: 90
score: {
english:78,math:90}
salarys:
- 7839
- 89374
pet:
name: 阿狗
weight: 45
allPets:
sick:
- {
name: 阿狗, weigth: 99.9}
- name: 阿毛
weight: 9.3
- name: 阿虫
weight: 77.7
health:
- {
name: 阿三, weigth: 99.9 }
- name: 阿四
weight: 9.3
- name: 阿五
weight: 77.7
字符串无需加引号,如果要加,单引号’'、双引号""表示字符串内容会被 转义、不转义
以下是理解:
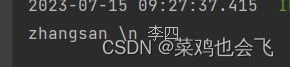
username: “zhangsan \n 李四”
username: ‘zhangsan \n 李四’
总结:单引号会将\n作为字符串输出,双引号会将\n作为换行输出
双引号不会转义,单引号会转义
21、配置文件-自定义类绑定的配置提示
You can easily generate your own configuration metadata file from items annotated with
@ConfigurationPropertiesby using thespring-boot-configuration-processorjar. The jar includes a Java annotation processor which is invoked as your project is compiled.——link
自定义的类和配置文件绑定一般没有提示。若要提示,添加如下依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<!-- 下面插件作用是工程打包时,不将spring-boot-configuration-processor打进包内,让其只在编码的时候有用 -->
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
22、web场景-web开发简介
Spring Boot provides auto-configuration for Spring MVC that works well with most applications.(大多场景我们都无需自定义配置)
The auto-configuration adds the following features on top of Spring’s defaults:
-
Inclusion of
ContentNegotiatingViewResolverandBeanNameViewResolverbeans.- 内容协商视图解析器和BeanName视图解析器
-
Support for serving static resources, including support for WebJars (covered later in this document)).
- 静态资源(包括webjars)
-
Automatic registration of
Converter,GenericConverter, andFormatterbeans.- 自动注册
Converter,GenericConverter,Formatter
- 自动注册
-
Support for
HttpMessageConverters(covered later in this document).- 支持
HttpMessageConverters(后来我们配合内容协商理解原理)
- 支持
-
Automatic registration of
MessageCodesResolver(covered later in this document).- 自动注册
MessageCodesResolver(国际化用)
- 自动注册
-
Static
index.htmlsupport.- 静态index.html 页支持
-
Custom
Faviconsupport (covered later in this document).- 自定义
Favicon
- 自定义
-
Automatic use of a
ConfigurableWebBindingInitializerbean (covered later in this document).- 自动使用
ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer,(DataBinder负责将请求数据绑定到JavaBean上)
- 自动使用
If you want to keep those Spring Boot MVC customizations and make more MVC customizations (interceptors, formatters, view controllers, and other features), you can add your own
@Configurationclass of typeWebMvcConfigurerbut without@EnableWebMvc.不用@EnableWebMvc注解。使用
@Configuration+WebMvcConfigurer自定义规则
If you want to provide custom instances of
RequestMappingHandlerMapping,RequestMappingHandlerAdapter, orExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver, and still keep the Spring Boot MVC customizations, you can declare a bean of typeWebMvcRegistrationsand use it to provide custom instances of those components.声明
WebMvcRegistrations改变默认底层组件
If you want to take complete control of Spring MVC, you can add your own
@Configurationannotated with@EnableWebMvc, or alternatively add your own@Configuration-annotatedDelegatingWebMvcConfigurationas described in the Javadoc of@EnableWebMvc.使用
@EnableWebMvc+@Configuration+DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration 全面接管SpringMVC
23、web场景-静态资源规则与定制化
静态资源目录
只要静态资源放在类路径下: called /static (or /public or /resources or /META-INF/resources
访问 : 当前项目根路径/ + 静态资源名
原理: 静态映射/**。
请求进来,先去找Controller看能不能处理。不能处理的所有请求又都交给静态资源处理器。静态资源也找不到则响应404页面。
也可以改变默认的静态资源路径,/static,/public,/resources, /META-INF/resources失效
resources:
static-locations: [classpath:/haha/]
静态资源访问前缀
spring:
mvc:
static-path-pattern: /res/**
当前项目 + static-path-pattern + 静态资源名 = 静态资源文件夹下找
http://localhost:8024/res/1.png
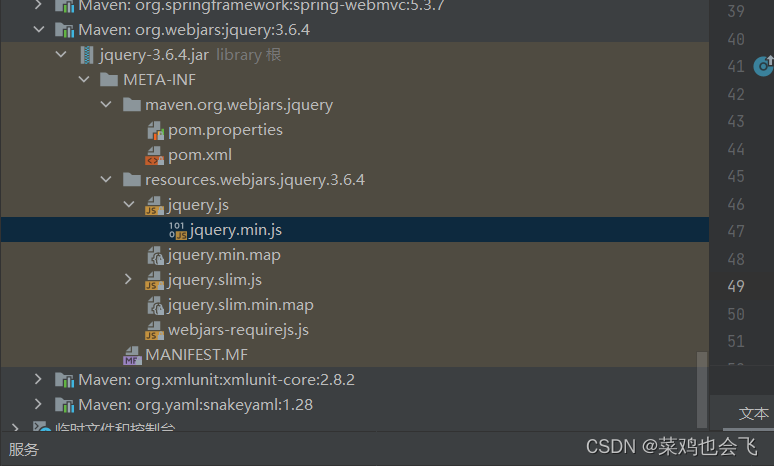
webjar
自动映射
可用jar方式添加css,js等资源文件,
例如,添加jquery
<dependency>
<groupId>org.webjars</groupId>
<artifactId>jquery</artifactId>
<version>3.5.1</version>
</dependency>
访问地址:http://localhost:8080/webjars/jquery/3.5.1/jquery.js 后面地址要按照依赖里面的包路径。
24、web场景-welcome与favicon功能
欢迎页支持
-
静态资源路径下 index.html。
- 可以配置静态资源路径
- 但是不可以配置静态资源的访问前缀。否则导致 index.html不能被默认访问
spring:
# mvc:
# static-path-pattern: /res/** 这个会导致welcome page功能失效
resources:
static-locations: [classpath:/haha/]
- controller能处理/index。
自定义Favicon
指网页标签上的小图标。
favicon.ico 放在静态资源目录下即可。
spring:
# mvc:
# static-path-pattern: /res/** 这个会导致 Favicon 功能失效
25、web场景-【源码分析】-静态资源原理
- SpringBoot启动默认加载 xxxAutoConfiguration 类(自动配置类)
- SpringMVC功能的自动配置类
WebMvcAutoConfiguration,生效
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass({
Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class)
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10)
@AutoConfigureAfter({
DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class,
ValidationAutoConfiguration.class })
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {
...
}
- 给容器中配置的内容:
- 配置文件的相关属性的绑定:WebMvcProperties==spring.mvc、ResourceProperties==spring.resources
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Import(EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({
WebMvcProperties.class, ResourceProperties.class })
@Order(0)
public static class WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter implements WebMvcConfigurer {
...
}
配置类只有一个有参构造器
有参构造器所有参数的值都会从容器中确定
public WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter(WebProperties webProperties, WebMvcProperties mvcProperties,
ListableBeanFactory beanFactory, ObjectProvider<HttpMessageConverters> messageConvertersProvider,
ObjectProvider<ResourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer> resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizerProvider,
ObjectProvider<DispatcherServletPath> dispatcherServletPath,
ObjectProvider<ServletRegistrationBean<?>> servletRegistrations) {
this.mvcProperties = mvcProperties;
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
this.messageConvertersProvider = messageConvertersProvider;
this.resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer = resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizerProvider.getIfAvailable();
this.dispatcherServletPath = dispatcherServletPath;
this.servletRegistrations = servletRegistrations;
智能推荐
文本分类特征提取之Word2Vec-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读4.4w次,点赞11次,收藏56次。分类问题是人类所面临的一个非常重要且具有普遍意义的问题,我们生活中的很多问题归根到底都是分类问题。文本分类就是根据文本内容将其分到合适的类别,它是自然语言处理的一个十分重要的问题。文本分类主要应用于信息检索,机器翻译,自动文摘,信息过滤,邮件分类等任务。文本分类技术发展历史 1960-1970:那时主要通过人工+规则(关键词或者正则表达式)的方式,制定规则的人需要对某类目领域有足够的认知和了解。举_文本特征提取word2vec
libevent高并发网络编程 - 06_基于libevent的C++线程池实现_windows c++ 开发 客户端 libevent-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1k次。本文利用libevent,实现一个C++线程池,,可自定义用户任务类,继承于任务task基类,重写任务基类的纯虚函数实现多态。比如将定义定义处理客户端的请求任务类,实现对客户端请求的并发处理。工作队列:可以理解为线程的队列,一个线程同时可以处理一个任务,空闲的线程回从任务队列取出任务执行。当工作队列空时,线程会睡眠。任务队列:用户将任务加入任务队列,然后通知工作队列,取出一个任务到线程中执行。_windows c++ 开发 客户端 libevent
工作缺点和不足及措施_【工作中存在的问题和不足及改进措施】_工作中的不足与改进_工作中不足及改进措施...-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读3.4w次,点赞3次,收藏11次。篇一:《工作中存在的不足及改进措施》通过近一段时间的工作,反省自身,还存在许多不足和缺点,现将近期的工作、学习中存在的不足和缺点简要总结如下:1、自身的专业业务水平不高,事故应急处理能力不强.虽然通过学习和工作经验的积累,在业务水平上有了一定的提高,但业务水平和工作经验与其它老同志比还是比较低.在日常工作中偏重于日常生产工作,也忽视了自身思想素质的提高,工作中争强当先的意识不强.2、工作上满足于正..._工作不足之处及改进措施
java读取大数据量Excel按需读取(按需加载,速度快)_java 读取大文件excel-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2k次。常用的poi工具,如easy-excel,hutool读取excel是都是先将整个excel加载到内存中分析,然后再一行行遍历,当excel文件太大时读取的时间就会更长,如果我们只需要读取excel的前几行来进行预览就不能使用这种方式,应该按需读取。_java 读取大文件excel
HTML_常用标签测试_html标签检测-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读237次。HTML_常用标签测试_html标签检测
【优化模型】牛顿法求解非线性方程组-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读482次。牛顿法是一种用于求解非线性方程组的迭代优化方法。其基本原理是基于泰勒级数展开和一阶导数的近似,通过不断迭代修正初始猜测解来逼近方程组的解。Fx0其中,Fxf1xf2x...fnxT是一个多元函数,xx1x2...xnT是待求解的变量向量。牛顿法的基本思想是,在当前的迭代点xk处,用一个一阶泰勒展开来近似fixfix≈fixkj1∑n∂xj∂fixk。
随便推点
克里金插值法(kringing)与PHPnow集成开发环境_后端克里金插值分析-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读815次。文章目录摘要摘要_后端克里金插值分析
使用有道云笔记的三个技巧_有道云笔记如何建立 文档索引-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读3.3w次,点赞10次,收藏36次。我们在 Windows 操作系统中写文档,做笔记,通常使用 Windows 自带的记事本,可是记事本不支持插入图片,创建表格等功能,从而不得不使用 Office Word。不知道大家有没有这样的感觉,使用 Office Word 写文档,效率极低,需要一边敲字,一边使用鼠标排版,比如:在文章中给团队的名字“LSGO软件技术团队”加粗,就需要先用鼠标选中这个词语,然后点击工具栏中“B”形状的工具..._有道云笔记如何建立 文档索引
IP-guard 远程命令执行漏洞_ipg 漏洞-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读137次。IP-guard 远程命令执行漏洞_ipg 漏洞
IOT时代,数据安全更无侥幸-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读255次。2017年,全球数据泄露事件已不仅是呈翻倍的速度增长。16年的14亿条,到17年仅上半年的17亿条,这样的数据泄露规模你是否还在存在侥幸心理,就是那所谓的“怎么可能刚好落在我身上”。随着我们在工作、生活中的云化,就在今天,万物互联已经融入到我们每个人的生活中,相信在不就的将来,整个IOT时代也将会很快的到来。仔细回忆一下,今天我们所做的任何情都离不..._8,iot时代,数据安全有哪些新特征?
MySQL 详细学习教程【万字长文, 建议收藏】_mysql教程-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读6.7k次,点赞47次,收藏143次。存放文本时,也可以使用Text数据类型,可以将TEXT列视为VARCHAR列,注意Text不能有默认值,大小0-2^16字节;同一查询在同一事务中多次进行,由于其它提交事务所做的修改和删除,每次返回不同的结果集,则发生不可重复读;多个连接开启各自事务操作数据库中数据时,数据库系统要负责隔离操作,以保证各个连接在获取数据是的准确性;同一查询在同一个事务中多次执行,由于其它提交事务所做的插入操作,每次返回不同的结果集,此时发生幻读;同真是的表一样,视图包含列,其数据来自对应的真实表(基表)_mysql教程
GD32官方开发环境及固件库使用笔记(一)_gd32e23 开发环境-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读550次,点赞10次,收藏6次。GD32官方的开发环境(基于Eclipse)的使用。_gd32e23 开发环境