使用Java代码实现傅里叶变换_java傅立叶变黑白-程序员宅基地
说明
-
该代码源自java使用傅里叶变换,对其进行了部分优化,可以实现将灰度图像转换为频率域图像,以及从频率域恢复为原图像。
-
初次接触傅里叶算法,有很多新概念,理解起来比较困难,需要多看几遍,参考链接都在文章最后。
-
这边的代码逻辑其实很简单,就是输入一组复数数组,进行处理后,返回相同长度的复数数组,处理的算法和下面的公式有关,然后和三角函数没有太大关联,但想理清整个傅里叶变换,三角函数还是绕不过去的。
-
通过去除图像中的低频率来提取边缘,或者通过去除高频率来模糊图像已经实现了,在recover()方法里面,去除高频率需要手动去除注释。

代码
主类
package com.example.springboot01.util;
import org.junit.Test;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 代码参考:https://blog.csdn.net/wangjichen_1/article/details/51120194
*/
public class FourierTransformer {
@Test
public void test() throws IOException {
String fromPic = "C:\\Users\\Dell\\Pictures\\aaa.jpg";
BufferedImage bufferedImage = ImageIO.read(new File(fromPic));
// 转换为频率域图像
BufferedImage destImg = convert(bufferedImage);
// 从频率域恢复为原图片,未实现去除高频率功能
// BufferedImage destImg = recover(bufferedImage);
File newFile = new File("d:\\test10.jpg");
ImageIO.write(destImg, "jpg", newFile);
}
/**
* 生成频率域图像
* @param srcImage
* @return
*/
public BufferedImage convert(BufferedImage srcImage) {
int iw = srcImage.getWidth();
int ih = srcImage.getHeight();
int[] pixels = new int[iw * ih];
int[] newPixels;
srcImage.getRGB(0, 0, iw, ih, pixels, 0, iw);
// 赋初值
int w = 1;
int h = 1;
// 计算进行付立叶变换的宽度和高度(2的整数次方)
while (w * 2 <= iw) {
w *= 2;
}
while (h * 2 <= ih) {
h *= 2;
}
// 分配内存
// 从左往右,从上往下排序
Complex[] src = new Complex[h * w];
// 从左往右,从上往下排序
Complex[] dest = new Complex[h * w];
newPixels = new int[h * w];
for (int i = 0; i < h; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < w; j++) {
// 初始化src,dest
dest[i * w + j] = new Complex();
// 获取蓝色通道分量,也就是像素点的灰度值
src[i * w + j] = new Complex(pixels[i * iw + j] & 0xff, 0);
}
}
// 在y方向上进行快速傅立叶变换
//
// 一行一行的处理
// 处理完后第一列都是各自行里面的最大值
//
for (int i = 0; i < h; i++) {
Complex[] temp = new Complex[w];
for (int k = 0; k < w; k++) {
temp[k] = src[i * w + k];
}
temp = FFT.fft(temp);
for (int k = 0; k < w; k++) {
dest[i * w + k] = temp[k];
}
}
// 对x方向进行傅立叶变换
// 一列一列的处理,从左往右
// 处理完后第一行都是各自列里面的最大值
for (int i = 0; i < w; i++) {
Complex[] temp = new Complex[h];
for (int k = 0; k < h; k++) {
temp[k] = dest[k * w + i];
}
temp = FFT.fft(temp);
for (int k = 0; k < h; k++) {
dest[k * w + i] = temp[k];
}
}
// 打印傅里叶频率域图像
for (int i = 0; i < h; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < w; j++) {
// 从左到右,从上到下遍历
double re = dest[i * w + j].re;
double im = dest[i * w + j].im;
int ii = 0, jj = 0;
// 缩小数值,方便展示
int temp = (int) (Math.sqrt(re * re + im * im) / 100);
// 用十字将图像切割为4等分,然后每个部分旋转180度,再拼接起来,方便观察
if (i < h / 2) {
ii = i + h / 2;
} else {
ii = i - h / 2;
}
if (j < w / 2) {
jj = j + w / 2;
} else {
jj = j - w / 2;
}
newPixels[ii * w + jj] = (clamp(temp) << 16) | (clamp(temp) << 8) | clamp(temp);;
}
}
BufferedImage destImg = new BufferedImage(w, h, BufferedImage.TYPE_BYTE_GRAY);
destImg.setRGB(0, 0, w, h, newPixels, 0, w);
return destImg;
}
/**
* 从频率还原为图像
* 已经实现了通过去除低频率提取边缘和通过去除高频率模糊图像两个功能
* @param srcImage
* @return
*/
public BufferedImage recover(BufferedImage srcImage) {
int iw = srcImage.getWidth();
int ih = srcImage.getHeight();
int[] pixels = new int[iw * ih];
int[] newPixels;
srcImage.getRGB(0, 0, iw, ih, pixels, 0, iw);
// 赋初值
int w = 1;
int h = 1;
// 计算进行付立叶变换的宽度和高度(2的整数次方)
while (w * 2 <= iw) {
w *= 2;
}
while (h * 2 <= ih) {
h *= 2;
}
// 分配内存
// 从左往右,从上往下排序
Complex[] src = new Complex[h * w];
// 从左往右,从上往下排序
Complex[] dest = new Complex[h * w];
newPixels = new int[h * w];
for (int i = 0; i < h; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < w; j++) {
// 初始化src,dest
dest[i * w + j] = new Complex();
// 获取蓝色通道分量,也就是像素点的灰度值
src[i * w + j] = new Complex(pixels[i * iw + j] & 0xff, 0);
}
}
// 在y方向上进行快速傅立叶变换
//
// 先一行一行的处理
// 处理完后第一列都是各自行里面的最大值
//
for (int i = 0; i < h; i++) {
Complex[] temp = new Complex[w];
for (int k = 0; k < w; k++) {
temp[k] = src[i * w + k];
}
temp = FFT.fft(temp);
for (int k = 0; k < w; k++) {
dest[i * w + k] = temp[k];
}
}
// 对x方向进行傅立叶变换
// 再一列一列的处理,从左往右
// 处理完后第一行都是各自列里面的最大值
for (int i = 0; i < w; i++) {
Complex[] temp = new Complex[h];
for (int k = 0; k < h; k++) {
temp[k] = dest[k * w + i];
}
temp = FFT.fft(temp);
for (int k = 0; k < h; k++) {
dest[k * w + i] = temp[k];
}
}
// 去除指定频率部分,然后还原为图像
int halfWidth = w/2;
int halfHeight = h/2;
// 比例越小,边界越突出
double res = 0.24;
// 比例越大,图片越模糊
double del = 0.93;
// 先对列进行逆傅里叶变换,并去除指定频率。和傅里叶变换顺序相反
for (int i = 0; i < w; i++) {
Complex[] temp = new Complex[h];
for (int k = 0; k < h; k++) {
// 去除低频率,保留边缘,因为频率图尚未做十字切割并分别旋转180度,所以此时图像dest[] 的四个角落是低频率,而中心部分是高频率
// 第一个点(0,0)不能删除,删掉后整张图片就变黑了
if (i == 0 && k == 0) {
temp[k] = dest[k * w + i];
} else if ((i <res*halfWidth && k < res*halfHeight) || (i <res*halfWidth && k > (1-res)*halfHeight)
|| (i > (1-res)*halfWidth && k <res*halfHeight) || (i > (1-res)*halfWidth && k > (1-res)*halfHeight)) {
temp[k] = new Complex(0, 0);
} else {
temp[k] = dest[k * w + i];
}
// 去除高频率,模糊图像。和去除低频率代码冲突,需要先屏蔽上面去除低频率的代码才能执行
/*if ((i > ((1-del)*halfWidth) && k > ((1-del)*halfHeight)) && (i <((1+del)*halfWidth) && k < ((1+del)*halfHeight))) {
temp[k] = new Complex(0, 0);
} else {
temp[k] = dest[k * w + i];
}*/
}
temp = FFT.ifft(temp);
for (int k = 0; k < h; k++) {
// 这边需要除以N,也就是temp[]的长度
dest[k * w + i].im = temp[k].im / h;
dest[k * w + i].re = temp[k].re / h;
}
}
// 再对行进行逆傅里叶变换
for (int i = 0; i < h; i++) {
Complex[] temp = new Complex[w];
for (int k = 0; k < w; k++) {
temp[k] = dest[i * w + k];
}
temp = FFT.ifft(temp);
for (int k = 0; k < w; k++) {
// 这边需要除以N,也就是temp[]的长度
dest[i * w + k].im = temp[k].im / w;
dest[i * w + k].re = temp[k].re / w;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < h; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < w; j++) {
// 从左到右,从上到下遍历
double re = dest[i * w + j].re;
int temp = (int) re;
newPixels[i * w + j] = (clamp(temp) << 16) | (clamp(temp) << 8) | clamp(temp);;
}
}
BufferedImage destImg = new BufferedImage(w, h, BufferedImage.TYPE_BYTE_GRAY);
destImg.setRGB(0, 0, w, h, newPixels, 0, w);
return destImg;
}
/**
* 如果像素点的值超过了0-255的范围,予以调整
*
* @param value 输入值
* @return 输出值
*/
private int clamp(int value) {
return value > 255 ? 255 : (Math.max(value, 0));
}
}
傅里叶变换类
package com.example.springboot01.util;
/**
* 快速傅里叶变换
* 傅里叶介绍参考:https://www.ruanx.net/fft/
* https://blog.csdn.net/YY_Tina/article/details/88361459
*/
public class FFT {
/**
* 快速傅里叶变换
* @param x
* @return
*/
// compute the FFT of x[], assuming its length is a power of 2
public static Complex[] fft(Complex[] x) {
int N = x.length;
// base case
if (N == 1)
return new Complex[] {
x[0] };
// radix 2 Cooley-Tukey FFT
if (N % 2 != 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("N is not a power of 2");
}
// fft of even terms
Complex[] even = new Complex[N / 2];
for (int k = 0; k < N / 2; k++) {
even[k] = x[2 * k];
}
Complex[] q = fft(even);
// fft of odd terms
Complex[] odd = even; // reuse the array
for (int k = 0; k < N / 2; k++) {
odd[k] = x[2 * k + 1];
}
Complex[] r = fft(odd);
// combine
Complex[] y = new Complex[N];
for (int k = 0; k < N / 2; k++) {
double kth = 2 * k * Math.PI / N;
Complex wk = new Complex(Math.cos(kth), Math.sin(kth));
y[k] = q[k].plus(wk.times(r[k]));
y[k + N / 2] = q[k].minus(wk.times(r[k]));
}
return y;
}
/**
* 逆快速傅里叶变换
* 与fft()相比,只修改了kth的值
* @param x
*/
public static Complex[] ifft(Complex[] x) {
int N = x.length;
// base case
if (N == 1)
return new Complex[] {
x[0] };
// radix 2 Cooley-Tukey FFT
if (N % 2 != 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("N is not a power of 2");
}
// fft of even terms
Complex[] even = new Complex[N / 2];
for (int k = 0; k < N / 2; k++) {
even[k] = x[2 * k];
}
Complex[] q = ifft(even);
// fft of odd terms
Complex[] odd = even; // reuse the array
for (int k = 0; k < N / 2; k++) {
odd[k] = x[2 * k + 1];
}
Complex[] r = ifft(odd);
// combine
Complex[] y = new Complex[N];
for (int k = 0; k < N / 2; k++) {
// 这边有区别
double kth = 2 * (N - k) * Math.PI / N;
Complex wk = new Complex(Math.cos(kth), Math.sin(kth));
y[k] = q[k].plus(wk.times(r[k]));
y[k + N / 2] = q[k].minus(wk.times(r[k]));
}
return y;
}
}
复数类
package com.example.springboot01.util;
/**
* 复数类
*/
public class Complex {
public double re; // the real part
public double im; // the imaginary part
public Complex() {
re = 0;
im = 0;
}
// create a new object with the given real and imaginary parts
public Complex(double real, double imag) {
re = real;
im = imag;
}
// return a string representation of the invoking Complex object
public String toString() {
if (im == 0) return re + "";
if (re == 0) return im + "i";
if (im < 0) return re + " - " + (-im) + "i";
return re + " + " + im + "i";
}
// return abs/modulus/magnitude and angle/phase/argument
public double abs() {
return Math.hypot(re, im); } // Math.sqrt(re*re + im*im)
public double phase() {
return Math.atan2(im, re); } // between -pi and pi
// return a new Complex object whose value is (this + b)
public Complex plus(Complex b) {
Complex a = this; // invoking object
double real = a.re + b.re;
double imag = a.im + b.im;
return new Complex(real, imag);
}
// return a new Complex object whose value is (this - b)
public Complex minus(Complex b) {
Complex a = this;
double real = a.re - b.re;
double imag = a.im - b.im;
return new Complex(real, imag);
}
// return a new Complex object whose value is (this * b)
public Complex times(Complex b) {
Complex a = this;
double real = a.re * b.re - a.im * b.im;
double imag = a.re * b.im + a.im * b.re;
return new Complex(real, imag);
}
// scalar multiplication
// return a new object whose value is (this * alpha)
public Complex times(double alpha) {
return new Complex(alpha * re, alpha * im);
}
// return a new Complex object whose value is the conjugate of this
public Complex conjugate() {
return new Complex(re, -im); }
// return a new Complex object whose value is the reciprocal of this
public Complex reciprocal() {
double scale = re*re + im*im;
return new Complex(re / scale, -im / scale);
}
// return the real or imaginary part
public double re() {
return re; }
public double im() {
return im; }
// return a / b
public Complex divides(Complex b) {
Complex a = this;
return a.times(b.reciprocal());
}
// return a new Complex object whose value is the complex exponential of this
public Complex exp() {
return new Complex(Math.exp(re) * Math.cos(im), Math.exp(re) * Math.sin(im));
}
// return a new Complex object whose value is the complex sine of this
public Complex sin() {
return new Complex(Math.sin(re) * Math.cosh(im), Math.cos(re) * Math.sinh(im));
}
// return a new Complex object whose value is the complex cosine of this
public Complex cos() {
return new Complex(Math.cos(re) * Math.cosh(im), -Math.sin(re) * Math.sinh(im));
}
// return a new Complex object whose value is the complex tangent of this
public Complex tan() {
return sin().divides(cos());
}
// a static version of plus
public static Complex plus(Complex a, Complex b) {
double real = a.re + b.re;
double imag = a.im + b.im;
Complex sum = new Complex(real, imag);
return sum;
}
}
效果图
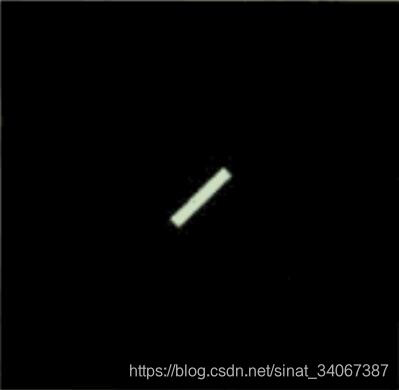
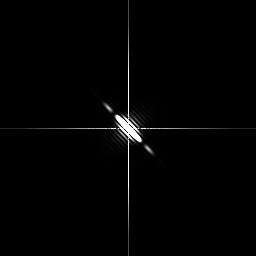
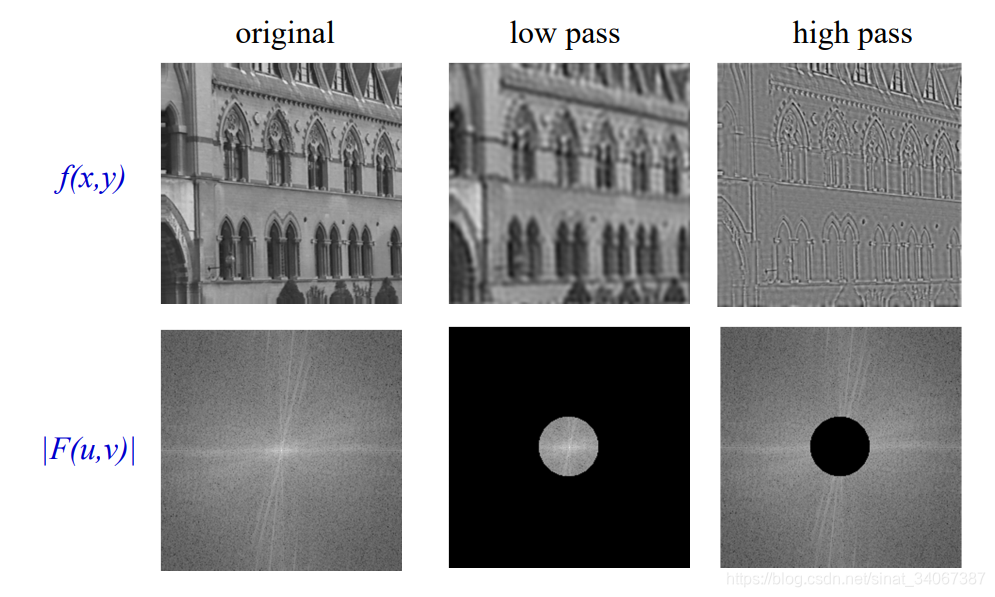
参考
java使用傅里叶变换,得到变换之后的傅里叶频谱图像。
快速傅里叶变换
快速傅里叶变换(FFT)和逆快速傅里叶变换(IFFT)
傅里叶分析之掐死教程(完整版)
图像傅里叶变换
二维傅里叶变换深度研究-图像与其频域关系
傅里叶变换在工程中的一些应用
形象理解二维傅里叶变换
智能推荐
使用nginx解决浏览器跨域问题_nginx不停的xhr-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1k次。通过使用ajax方法跨域请求是浏览器所不允许的,浏览器出于安全考虑是禁止的。警告信息如下:不过jQuery对跨域问题也有解决方案,使用jsonp的方式解决,方法如下:$.ajax({ async:false, url: 'http://www.mysite.com/demo.do', // 跨域URL ty..._nginx不停的xhr
在 Oracle 中配置 extproc 以访问 ST_Geometry-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2k次。关于在 Oracle 中配置 extproc 以访问 ST_Geometry,也就是我们所说的 使用空间SQL 的方法,官方文档链接如下。http://desktop.arcgis.com/zh-cn/arcmap/latest/manage-data/gdbs-in-oracle/configure-oracle-extproc.htm其实简单总结一下,主要就分为以下几个步骤。..._extproc
Linux C++ gbk转为utf-8_linux c++ gbk->utf8-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.5w次。linux下没有上面的两个函数,需要使用函数 mbstowcs和wcstombsmbstowcs将多字节编码转换为宽字节编码wcstombs将宽字节编码转换为多字节编码这两个函数,转换过程中受到系统编码类型的影响,需要通过设置来设定转换前和转换后的编码类型。通过函数setlocale进行系统编码的设置。linux下输入命名locale -a查看系统支持的编码_linux c++ gbk->utf8
IMP-00009: 导出文件异常结束-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读750次。今天准备从生产库向测试库进行数据导入,结果在imp导入的时候遇到“ IMP-00009:导出文件异常结束” 错误,google一下,发现可能有如下原因导致imp的数据太大,没有写buffer和commit两个数据库字符集不同从低版本exp的dmp文件,向高版本imp导出的dmp文件出错传输dmp文件时,文件损坏解决办法:imp时指定..._imp-00009导出文件异常结束
python程序员需要深入掌握的技能_Python用数据说明程序员需要掌握的技能-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读143次。当下是一个大数据的时代,各个行业都离不开数据的支持。因此,网络爬虫就应运而生。网络爬虫当下最为火热的是Python,Python开发爬虫相对简单,而且功能库相当完善,力压众多开发语言。本次教程我们爬取前程无忧的招聘信息来分析Python程序员需要掌握那些编程技术。首先在谷歌浏览器打开前程无忧的首页,按F12打开浏览器的开发者工具。浏览器开发者工具是用于捕捉网站的请求信息,通过分析请求信息可以了解请..._初级python程序员能力要求
Spring @Service生成bean名称的规则(当类的名字是以两个或以上的大写字母开头的话,bean的名字会与类名保持一致)_@service beanname-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读7.6k次,点赞2次,收藏6次。@Service标注的bean,类名:ABDemoService查看源码后发现,原来是经过一个特殊处理:当类的名字是以两个或以上的大写字母开头的话,bean的名字会与类名保持一致public class AnnotationBeanNameGenerator implements BeanNameGenerator { private static final String C..._@service beanname
随便推点
二叉树的各种创建方法_二叉树的建立-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读6.9w次,点赞73次,收藏463次。1.前序创建#include<stdio.h>#include<string.h>#include<stdlib.h>#include<malloc.h>#include<iostream>#include<stack>#include<queue>using namespace std;typed_二叉树的建立
解决asp.net导出excel时中文文件名乱码_asp.net utf8 导出中文字符乱码-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读7.1k次。在Asp.net上使用Excel导出功能,如果文件名出现中文,便会以乱码视之。 解决方法: fileName = HttpUtility.UrlEncode(fileName, System.Text.Encoding.UTF8);_asp.net utf8 导出中文字符乱码
笔记-编译原理-实验一-词法分析器设计_对pl/0作以下修改扩充。增加单词-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.1k次,点赞4次,收藏23次。第一次实验 词法分析实验报告设计思想词法分析的主要任务是根据文法的词汇表以及对应约定的编码进行一定的识别,找出文件中所有的合法的单词,并给出一定的信息作为最后的结果,用于后续语法分析程序的使用;本实验针对 PL/0 语言 的文法、词汇表编写一个词法分析程序,对于每个单词根据词汇表输出: (单词种类, 单词的值) 二元对。词汇表:种别编码单词符号助记符0beginb..._对pl/0作以下修改扩充。增加单词
android adb shell 权限,android adb shell权限被拒绝-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读773次。我在使用adb.exe时遇到了麻烦.我想使用与bash相同的adb.exe shell提示符,所以我决定更改默认的bash二进制文件(当然二进制文件是交叉编译的,一切都很完美)更改bash二进制文件遵循以下顺序> adb remount> adb push bash / system / bin /> adb shell> cd / system / bin> chm..._adb shell mv 权限
投影仪-相机标定_相机-投影仪标定-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读6.8k次,点赞12次,收藏125次。1. 单目相机标定引言相机标定已经研究多年,标定的算法可以分为基于摄影测量的标定和自标定。其中,应用最为广泛的还是张正友标定法。这是一种简单灵活、高鲁棒性、低成本的相机标定算法。仅需要一台相机和一块平面标定板构建相机标定系统,在标定过程中,相机拍摄多个角度下(至少两个角度,推荐10~20个角度)的标定板图像(相机和标定板都可以移动),即可对相机的内外参数进行标定。下面介绍张氏标定法(以下也这么称呼)的原理。原理相机模型和单应矩阵相机标定,就是对相机的内外参数进行计算的过程,从而得到物体到图像的投影_相机-投影仪标定
Wayland架构、渲染、硬件支持-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.2k次。文章目录Wayland 架构Wayland 渲染Wayland的 硬件支持简 述: 翻译一篇关于和 wayland 有关的技术文章, 其英文标题为Wayland Architecture .Wayland 架构若是想要更好的理解 Wayland 架构及其与 X (X11 or X Window System) 结构;一种很好的方法是将事件从输入设备就开始跟踪, 查看期间所有的屏幕上出现的变化。这就是我们现在对 X 的理解。 内核是从一个输入设备中获取一个事件,并通过 evdev 输入_wayland